world.wikisort.org - USA
The Northwest Angle, known simply as the Angle by locals, and coextensive with Angle Township, is a pene-exclave of northern Lake of the Woods County, Minnesota. Except for surveying errors,[1] it is the only place in the contiguous United States north of the 49th parallel, which forms the border between the U.S. and Canada from the Northwest Angle westward to the Strait of Georgia (between the U.S. state of Washington and the province of British Columbia). The land area of the Angle is separated from the rest of Minnesota by Lake of the Woods, but shares a land border with Canada. It is one of six non-island locations in the 48 contiguous states that are practical exclaves of the U.S. It is the northernmost township in Minnesota and contains the northernmost point in the contiguous 48 states. The unincorporated community of Angle Inlet is in the Northwest Angle.
This article needs additional citations for verification. (January 2013) |
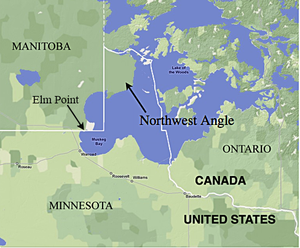
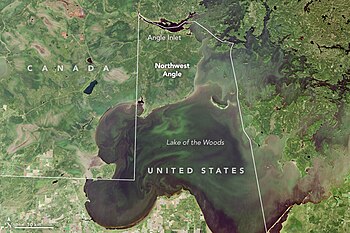
Seventy percent of the land of the Angle is held in trust by the Red Lake Indian Reservation (Ojibwa).[2]
Although the Angle is listed as one of several distinct regions of Minnesota, its total population was 119 at the 2010 census.[3] The area is mostly water and the land is mostly forest.
Origin
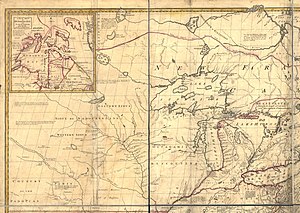
Angle Township was designated as territory of the United States because negotiators of the initial Canada–U.S. border misunderstood the geography of the area. Benjamin Franklin and British representatives relied on the Mitchell Map of colonial American geographer John Mitchell, which did not indicate the source of the Mississippi River—thought to lie some distance to the northwest—or the true shape of Lake of the Woods, which was instead shown as roughly oval. The 1783 Treaty of Paris thus stated that the boundary between U.S. territory and the British possessions to the north would run "...through the Lake of the Woods to the northwesternmost point thereof, and from thence on a due west course to the river Mississippi..."
But the source of the Mississippi River, Lake Itasca (then unknown to European explorers), lies almost due south of Lake of the Woods, rather than north and west of it. Additionally, the irregular actual shape of the lake made the identification of its northwest corner difficult. A survey team led by David Thompson in 1824 mapped the lake and found four possibilities, but did not conclusively declare one location.[4] In 1825, a German astronomer in British service, Johann Ludwig Tiarks, surveyed the lake. Tiarks identified two possibilities for the northwesternmost point on the lake, based on Thompson's maps: the Angle Inlet and Rat Portage. To determine which point was the most northwestern, he drew a line from each point in the southwest–northeast direction. If the line intersected the lake at any point, it was not the most northwestern point. Tiarks determined that the only such line that did not intersect the lake was at the edge of a pond on the Angle Inlet.[4] A 1940 academic study documents this point as being in the vicinity of 49.39°N 95.153°W (NAD83).[5]
In the Anglo-American Convention of 1818, the error regarding the Mississippi River was corrected by having the boundary continue due south from the northwest point of the lake, but only to the 49th parallel and then westward along it. The Webster–Ashburton Treaty of 1842 reaffirmed this border. However, the placement of the northwestern corner and shape of the lake meant that this north–south line cut off a section of U.S. territory to its east, now known as the Northwest Angle.
Geography

According to the United States Census Bureau, Angle Township has a total area of 596.3 square miles (1,544.5 km2) of which 123.09 square miles (318.81 km2) is land and 473.2 square miles (1,225.7 km2) (79.36%) is water. The land includes several islands, including Oak Island, and two small capes that are below (south of) the 49th parallel north in the extreme southwest part of the township, one of which is known as Elm Point, south of the southeast corner of Manitoba, and not far from the northeast corner of Roseau County. Of the 2000 census population of 152, there were 118 living on the mainland, and 34 persons on the islands in Lake of the Woods. All of the populated islands are north of the 49th parallel.
The mainland portion of the township north of the 49th parallel has an area of 116.632 square miles (302.08 km2). The total land area of all islands is 6.303 square miles (16.32 km2), and the two capes total 100 acres (0.16 sq mi; 40.47 ha). The township has the last one-room public school in the state.
Elm Point, in Lake of the Woods County, is a small cape southwest of the Northwest Angle. It borders Canada and is, together with a similar smaller cape to the west, separated by land from the continental United States.
Access

The Angle is accessible from the rest of Minnesota by one of two ways:
- The Angle can be reached without crossing the international border by crossing the Lake of the Woods. This can be done by boat when the lake is free of ice, by ice road in the winter or by flying over it in a plane. No automobile ferries currently operate on the lake, so vehicles coming from the rest of Minnesota cannot reach the Angle without crossing the border except in winter. While the ice is forming in late autumn and breaking up in the spring, the lake's surface cannot be crossed safely – at these times domestic access to the Angle is possible only by air. In January 2021, local US interests opened a 22-mile (35 km) toll road across the ice, at a round-trip charge of US$120 to $145, because the Canadian border was closed by COVID-19 pandemic restrictions. It was again opened, and lengthened to 37 miles (60 km) of road, in January 2022, and the toll set at $250. [6]
- To reach the Angle by land, travelers take Minnesota State Highway 313 northbound (Warroad, Minnesota, to Sprague, Manitoba) across the Warroad-Sprague Border Crossing[7] connecting to Manitoba Highway 12 at the border, then to Provincial Road 308, to Provincial Road 525, then finally crossing back into the United States in the Northwest Angle south of Angle Inlet, Minnesota (Angle Inlet Township). The distance from Warroad or Roseau to the Angle proper is approximately 63 miles (101 km) through Minnesota and Manitoba back to the Angle's U.S. border. It is approximately 10 miles (16 km) from the actual border (intersection of Manitoba 525 and NWA Road Dawson) to the rural developments of the Northwest Angle. The border crossing is unstaffed. Travelers using the single gravel road in and out of the Angle are expected to use a telephone at Jim's Corner,[8] Youngs Bay Marina, or Carlsons Landing to contact Canadian or U.S. Customs and make their declarations.
Political issues
Because of laws restricting fishing, some residents of the Northwest Angle suggested leaving the United States and joining Canada in 1997. The following year, then-U.S. representative Collin Peterson of Minnesota proposed legislation to allow the residents of the Northwest Angle, which was part of his district, to vote on seceding from the United States and joining Canada. This angered the leaders of Red Lake Indian Reservation, which holds most of the Northwest Angle's land.[9][10] The incident resulted in fishing regulations being better synchronized across these waters.[11]
Demographics
As of the census[12] of 2010, there were 119 people, 66 households, and 37 families residing in the Angle. There were 404 housing units. The racial makeup of the township was 99.2% White (118 out of 119). Native American or Alaska Native of any race were 0.8% of the population (that is, 1 person).
Out of the 66 households, 10.9% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 54.5% were married couples living together, 0% had a female householder with no husband present, and 43.9% were non-families. 37.9% of all households were made up of individuals, and 3% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 1.80, and the average family size was 2.32.
In the Angle the population is spread out, with 10.1% under the age of 18, 0.8% from 18 to 24, 10.1% from 25 to 44, 51.3% from 45 to 64, and 27.6% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 50 years. For every 100 females, there were 120.3 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 124.1 males.
The median income for a household in the township was $28,500, and the median income for a family was $31,250. Males had a median income of $28,500 versus $21,250 for females. The per capita income for the township was $13,932. About 13.3% of families and 12.3% of the population were below the poverty line, including none of those under the age of 18 or 65 and older.
Climate
According to the Köppen climate classification system, the Northwest Angle has a Warm-summer, Humid continental climate (Dfb). Dfb climates are characterized by at least one month having an average mean temperature ≤ 32.0 °F (0.0 °C), at least four months with an average mean temperature ≥ 50.0 °F (10.0 °C), all months with an average mean temperature < 71.6 °F (22.0 °C) and no significant precipitation difference between seasons. Although most summer days are comfortably humid in the Northwest Angle, episodes of heat and high humidity can occur with heat index values > 90 °F (32 °C). The Northwest Angle weather station is one of the newer ones, as it only began keeping records in 1981, in contrast with nearby International Falls which has been keeping records for over a century. Since 1981, the highest air temperature was 96.8 °F (36.0 °C) on July 5, 1988, and the highest daily average mean dew point was 73.1 °F (22.8 °C) on 4 August 2001. Since 1981, the wettest calendar day was 4.11 inches (104 mm) on June 9, 2002. During the winter months, the average annual extreme minimum air temperature is −38.0 °F (−38.9 °C).[13] Since 1981, the coldest air temperature was −47.3 °F (−44.1 °C) on February 2, 2002. Episodes of extreme cold and wind can occur with wind chill values under −55 °F (−48 °C). The average annual snowfall total (Sep–May) is between 48 inches (122 cm) and 54 inches (137 cm).
| Climate data for Northwest Angle, Elevation 1,096 ft (334 m), 1981-2010 normals, extremes 1981-2018 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 46.7 (8.2) |
51.5 (10.8) |
74.0 (23.3) |
84.9 (29.4) |
90.4 (32.4) |
95.0 (35.0) |
96.8 (36.0) |
96.1 (35.6) |
93.4 (34.1) |
82.9 (28.3) |
69.3 (20.7) |
48.9 (9.4) |
96.8 (36.0) |
| Average high °F (°C) | 13.4 (−10.3) |
20.4 (−6.4) |
32.5 (0.3) |
48.5 (9.2) |
62.5 (16.9) |
70.9 (21.6) |
76.3 (24.6) |
74.5 (23.6) |
64.4 (18.0) |
49.8 (9.9) |
32.6 (0.3) |
18.0 (−7.8) |
47.1 (8.4) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 3.4 (−15.9) |
9.5 (−12.5) |
22.0 (−5.6) |
38.2 (3.4) |
51.8 (11.0) |
61.3 (16.3) |
65.9 (18.8) |
64.4 (18.0) |
54.7 (12.6) |
41.5 (5.3) |
25.5 (−3.6) |
9.6 (−12.4) |
37.4 (3.0) |
| Average low °F (°C) | −6.5 (−21.4) |
−1.4 (−18.6) |
11.4 (−11.4) |
27.8 (−2.3) |
41.1 (5.1) |
51.6 (10.9) |
55.4 (13.0) |
54.3 (12.4) |
44.9 (7.2) |
33.2 (0.7) |
18.4 (−7.6) |
1.1 (−17.2) |
27.7 (−2.4) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −45.2 (−42.9) |
−47.3 (−44.1) |
−29.4 (−34.1) |
−2.7 (−19.3) |
20.4 (−6.4) |
32.1 (0.1) |
36.7 (2.6) |
32.8 (0.4) |
24.5 (−4.2) |
4.8 (−15.1) |
−28.0 (−33.3) |
−35.9 (−37.7) |
−47.3 (−44.1) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 0.91 (23) |
0.65 (17) |
0.91 (23) |
1.27 (32) |
2.97 (75) |
4.35 (110) |
3.68 (93) |
3.27 (83) |
2.76 (70) |
2.07 (53) |
1.32 (34) |
0.98 (25) |
25.14 (639) |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 83.0 | 80.5 | 73.1 | 61.4 | 62.0 | 70.4 | 74.6 | 75.3 | 77.2 | 76.9 | 85.3 | 87.7 | 75.6 |
| Average dew point °F (°C) | −0.6 (−18.1) |
4.7 (−15.2) |
14.7 (−9.6) |
26.1 (−3.3) |
39.2 (4.0) |
51.6 (10.9) |
57.6 (14.2) |
56.4 (13.6) |
47.7 (8.7) |
34.8 (1.6) |
21.7 (−5.7) |
6.7 (−14.1) |
30.2 (−1.0) |
| Source: PRISM[14] | |||||||||||||
Ecology

According to the A. W. Kuchler U.S. potential natural vegetation types, the Northwest Angle would have a dominant vegetation type of Great Lakes Spruce/Fir (93) with a dominant vegetation form of Northern Conifer Forest (22).[15] The plant hardiness zone is 3a with an average annual extreme minimum air temperature of −38.0 °F (−38.9 °C).[13] The spring bloom typically peaks in mid-May and fall color usually peaks in late September.
Representation in other media
- Ernie Pyle wrote several columns about the Northwest Angle and its residents, which were collected in Home Country (1947), published posthumously.
- The American writer Tim O'Brien set his bestselling novel In the Lake of the Woods (1994) in the Angle. His short story "On the Rainy River" is also set there.
- William Kent Krueger's novel Northwest Angle (2011) is set in the area.
- The Danny Orlis series of books, a Christian fiction series for youth, were largely set in the Northwest Angle.
See also
- Border irregularities of the United States
- Extreme points of the United States
- Height of Land Portage
- Point Roberts, Washington, another practical exclave
References
- Jacobs, Frank (2011-11-28). "A Not-So-Straight Story". Opinionator. Retrieved 2021-03-15.
- "About the Red Lake Indian Reservation". Red Lake Net News. Archived from the original on November 15, 2010.
- "2010 Census Redistricting Data (Public Law 94-171) Summary File - County Subdivision". American FactFinder. United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 1 May 2011.[dead link]
- Lass, William (1980). Minnesota's Boundary with Canada: Its Evolution Since 1783. Minnesota Historical Society Press. pp. 47, 48. ISBN 0873511530.
- Boggs, Samuel Whittemore (1940). International boundaries: A study of boundary functions and problems. New York: Columbia University Press. pp. 48, 49. Retrieved 13 February 2019.
- "Ice highway connecting Warroad with Northwest Angle is back for second year". Star Tribune.
- "Chapter 5: The 49th Parallel". United Divide: A Linear Portrait of the USA/Canada Border. The Center for Land Use Interpretation. Winter 2015.
- "JIM'S CORNER, MINNESOTA". The Center for Land Use Interpretation. Winter 2020.
- Radil, Amy (August 17, 1998). "The Northwest Angle". Minnesota Public Radio.
- "Campaign 2006: U.S. Congress: 7th District: Collin Peterson". Minnesota Public Radio.
- Stoddard, Grant (January–February 2011). "The Lost Canadians". The Walrus. pp. 24–31. Archived from the original on 2012-12-23. Retrieved 2013-04-15.
- "U.S. Census website". Retrieved 2008-01-31.
- "USDA Interactive Plant Hardiness Map". United States Department of Agriculture. Archived from the original on June 18, 2021. Retrieved October 7, 2019.
- "PRISM Climate Group, Oregon State University". Retrieved October 7, 2019.
- "U.S. Potential Natural Vegetation, Original Kuchler Types, v2.0 (Spatially Adjusted to Correct Geometric Distortions)". Retrieved October 7, 2019.
Further reading
- Archived at Ghostarchive and the Wayback Machine: "America's small town in Canada". CBS Sunday Morning. 2016-05-01.
External links
- Northwest Angle in MNopedia, Minnesota Historical Society
- Angle Inlet School: Minnesota's last one-room school
- "The Northwest Angle" (radio programme transcript), Minnesota Public Radio
- Boundary Commission Coordinates, International Boundary Commission
- "To the Nub", website – An account of an RV trip to Northwest Angle from Washington, DC
- Northwest Angle Trip Report Visit to the extreme northernmost point of the Angle.
- "Northwest Angle, Minnesota". NASA Earth Observatory newsroom. Archived from the original on 2006-10-01. Retrieved 2006-04-27.
На других языках
[de] Northwest Angle
Der Northwest Angle („Nordwestwinkel“), amtlich Angle Township, von Einheimischen auch kurz als The Angle bezeichnet, ist der nördlichste Teil des Lake of the Woods County im US-Bundesstaat Minnesota. Abgesehen von Alaska handelt es sich dabei um das einzige Gebiet der Vereinigten Staaten, das nördlich einer geographischen Breite von 49° liegt.- [en] Northwest Angle
Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии
