world.wikisort.org - Japan
Toyonaka (豊中市, Toyonaka-shi) is a city in Osaka Prefecture, Japan. The city was founded on October 15, 1936.
This article needs additional citations for verification. (May 2017) |
Toyonaka
豊中市 | |
|---|---|
Core city | |
 Toyonaka City Hall | |
 Flag  Seal | |
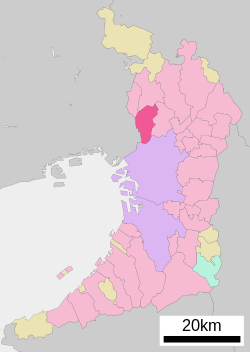 Location of Toyonaka in Osaka Prefecture | |
 Toyonaka Location in Japan | |
| Coordinates: 34°47′N 135°28′E | |
| Country | Japan |
| Region | Kansai |
| Prefecture | Osaka Prefecture |
| First official recorded | 684 AD |
| City Established | October 15, 1936 |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Keiichirō Asari |
| Area | |
| • Total | 36.38 km2 (14.05 sq mi) |
| Population (October 1, 2016) | |
| • Total | 396,014 |
| • Density | 11,000/km2 (28,000/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+09:00 (JST) |
| City hall address | 3-1-1 Nakasakurazuka, Toyonaka-shi, Osaka-fu 561-8501 |
| Climate | Cfa |
| Website | Official website |
| Symbols | |
| Flower | Rose |
| Tree | Sweet Osmanthus |

Geography
Climate
Toyonaka has a Humid subtropical climate (Köppen Cfa) characterized by warm summers and cool winters with light to no snowfall. The average annual temperature in Toyonaka is 16.4 °C (61.5 °F). The average annual rainfall is 1,326.3 mm (52.22 in) with July as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around 28.7 °C (83.7 °F), and lowest in January, at around 5.1 °C (41.2 °F).[1]
| Climate data for Toyonaka (1991−2020 normals, extremes 1977−present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 18.8 (65.8) |
22.2 (72.0) |
23.4 (74.1) |
30.8 (87.4) |
33.2 (91.8) |
37.9 (100.2) |
38.7 (101.7) |
39.9 (103.8) |
37.0 (98.6) |
33.9 (93.0) |
26.3 (79.3) |
23.7 (74.7) |
39.9 (103.8) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 9.6 (49.3) |
10.4 (50.7) |
14.1 (57.4) |
19.9 (67.8) |
25.0 (77.0) |
28.1 (82.6) |
31.8 (89.2) |
33.8 (92.8) |
29.6 (85.3) |
23.8 (74.8) |
17.8 (64.0) |
12.1 (53.8) |
21.3 (70.4) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 5.1 (41.2) |
5.7 (42.3) |
9.1 (48.4) |
14.5 (58.1) |
19.5 (67.1) |
23.3 (73.9) |
27.4 (81.3) |
28.7 (83.7) |
24.7 (76.5) |
18.7 (65.7) |
12.7 (54.9) |
7.4 (45.3) |
16.4 (61.5) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 0.7 (33.3) |
1.0 (33.8) |
4.0 (39.2) |
9.1 (48.4) |
14.3 (57.7) |
19.3 (66.7) |
23.8 (74.8) |
24.8 (76.6) |
20.7 (69.3) |
14.2 (57.6) |
7.8 (46.0) |
2.8 (37.0) |
11.9 (53.4) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −5.8 (21.6) |
−6.3 (20.7) |
−3.7 (25.3) |
−0.4 (31.3) |
4.6 (40.3) |
9.9 (49.8) |
15.7 (60.3) |
17.3 (63.1) |
10.8 (51.4) |
3.9 (39.0) |
0.0 (32.0) |
−4.5 (23.9) |
−6.3 (20.7) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 44.4 (1.75) |
59.3 (2.33) |
97.1 (3.82) |
98.2 (3.87) |
137.4 (5.41) |
180.1 (7.09) |
182.6 (7.19) |
122.8 (4.83) |
159.2 (6.27) |
127.1 (5.00) |
68.5 (2.70) |
49.6 (1.95) |
1,326.3 (52.22) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 5.4 | 6.2 | 9.2 | 8.8 | 9.7 | 11.1 | 10.6 | 7.2 | 9.9 | 8.5 | 5.8 | 6.0 | 98.4 |
| Source: Japan Meteorological Agency[2][1] | |||||||||||||
Neighboring municipalities
- Osaka Prefecture
- Yodogawa-ku, Osaka
- Suita
- Minoh
- Ikeda
- Hyōgo Prefecture
- Amagasaki
- Itami
Demographics
As of 2016[update], the city has an estimated population of 396,014 and a population density of 11,000 persons per km². The total area is 36.38 km².[citation needed] Its peak population was over 420,000.[citation needed]
Toyonaka is a residential area of Osaka Prefecture, and includes Senri New Town.
The city is easy to reach through various modes of transportation, and many of its residents commute daily into Osaka City to work. Osaka University and Osaka Music College have their campuses in Toyonaka.
The Harada Shinto shrine is located in Toyonaka, adjacent to the Hankyu Okamachi station. Founded during the reign of the Emperor Tenmu (672-686), the wooden shrine was rebuilt in 1652 and again in 1781. An important cultural property, it is known for its copse of camphor trees and it is the site of the popular Lion Festival each October.[3]
The Consulate-General of Russia in Osaka is located in Toyonaka.[4]
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1950 | 102,304 | — |
| 1955 | 127,678 | +24.8% |
| 1960 | 199,065 | +55.9% |
| 1965 | 291,936 | +46.7% |
| 1970 | 368,498 | +26.2% |
| 1975 | 398,384 | +8.1% |
| 1980 | 403,174 | +1.2% |
| 1985 | 413,213 | +2.5% |
| 1990 | 409,837 | −0.8% |
| 1995 | 398,908 | −2.7% |
| 2000 | 391,726 | −1.8% |
| 2005 | 386,623 | −1.3% |
| 2010 | 389,359 | +0.7% |
| 2015 | 395,479 | +1.6% |
| 2020 | 401,558 | +1.5% |
| Toyonaka population statistics[5] | ||
Transportation
Osaka International Airport is partially located in Toyonaka including its terminal, although it is more commonly associated with the city of Itami.
The city is served by the Osaka Monorail (Senri-Chūō Station, Shōji Station, Shibahara Station, Hotarugaike Station and Osaka Airport Station), the Kita-Osaka Kyūkō Railway (Senri-Chūō Station and Ryokuchi-kōen Station) and the Hankyu Takarazuka Line (Shōnai Station, Hattori-tenjin Station, Sone Station, Okamachi Station, Toyonaka Station and Hotarugaike Station). It is the second-largest city in Japan to lack service by any JR company, after Toyota.
Hankyu bus provides local bus service throughout Toyonaka and into neighboring cities. Most services connect with railway stations, especially Senri Chuo and Toyonaka. Some medium- and long-distance highway bus services are available from Senri Chuo and Osaka Airport.
Points of interest
- Hattori Ryokuchi Arboretum
- Hattori Ryokuchi Park
- Osaka University
- Open-Air Museum of Old Japanese Farm Houses
Sister cities
 San Mateo, California, United States
San Mateo, California, United States
Notable people
- Shōzō Endō - comedian
- Takashi Fujii - television performer
- Mai Hosho - actress [6]
- Tak Matsumoto - musician and guitarist (B'z)
- Yoshihiro Murai - governor of Miyagi prefecture (2005–present)
- Yukie Nishimura - pianist and composer
- Masashi Oguro - soccer player
- Panchan Rina - kickboxer
- Kaoru Shintani - manga artist
- Sanshiro Takagi - professional wrestler
- Naoki Tanaka - comedian
- Naoki Tanizaki - professional wrestler
- Osamu Tezuka - manga artist and animator
- Hitomi Yaida - singer and songwriter
- Unagi Sayaka - professional wrestler
References
- 気象庁 / 平年値(年・月ごとの値). JMA. Retrieved April 12, 2022.
- 観測史上1~10位の値(年間を通じての値). JMA. Retrieved April 12, 2022.
- http://www.nihon-kankou.or.jp.e.wp.hp.transer.com/osaka/detail/27203ba2212055492 [dead link]
- "List of Consulates in Kansai Area Archived 2008-09-23 at the Wayback Machine." Creation Core Higashi Osaka. Retrieved on January 15, 2009.
- Toyonaka population statistics
- 株式会社スポーツニッポン新聞社マルチメディア事業本部. 宝生舞 ~タレント名鑑~ ― スポニチ Sponichi Annex 芸能. www.sponichi.co.jp (in Japanese). Retrieved 2016-02-20.
External links
- Official website (in Japanese)
На других языках
- [en] Toyonaka
[es] Toyonaka
Toyonaka (豊中市, Toyonaka-shi?) es una ciudad ubicada en la prefectura de Osaka, Japón. En julio de 2019 tenía una población estimada de 399.731 habitantes y una densidad de población de 10.985 personas por km². Su área total es de 36,39 km².[ru] Тоёнака
Тоёна́ка (яп. 豊中市 Тоёнака-си) — Центральный город Японии, расположенный на реке Кандзаки в префектуре Осака. Площадь города составляет 36,38 км²[1], население — 395 023 человека (1 августа 2014)[2], плотность населения — 10 858,25 чел./км². Промышленный пригород Осаки. Развиты нефтехимическая, металлургическая промышленность, производство специальных транспортных средств (в том числе судов на подводных крыльях).Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии