world.wikisort.org - Thailand
Yasothon province (Thai: ยโสธร, pronounced [já.sǒː.tʰɔ̄ːn]), one of Thailand's seventy-six provinces (changwat), lies in central northeastern Thailand also called Isan. The province was established by the revolutionary council of Field Marshal Thanom Kittikachorn, after its Announcement No. 70 which came into force on 3 March 1972.
Yasothon
ยโสธร | |
|---|---|
Province | |
From left to right, top to bottom : Naga building at Vimarn Phaya Thean, Phra That Kuchan, Wat Maha That, St Michael's Church, Songyae, Phra That Kong Khao Noi, Rocket Festival | |
 Flag  Seal | |
| Nickname: Mueang Yot | |
 Map of Thailand highlighting Yasothon province | |
| Country | Thailand |
| Capital | Yasothon |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Chonlatee Yangtrong (since October 2020)[1] |
| Area | |
| • Total | 4,131 km2 (1,595 sq mi) |
| • Rank | Ranked 52nd |
| Population (2019)[3] | |
| • Total | 537,299 |
| • Rank | Ranked 48th |
| • Density | 130/km2 (300/sq mi) |
| • Rank | Ranked 34th |
| Human Achievement Index | |
| • HAI (2017) | 0.5790 "somewhat low" Ranked 46th |
| Time zone | UTC+7 (ICT) |
| Postal code | 35xxx |
| Calling code | 045 |
| ISO 3166 code | TH-35 |
| Website | www |
Neighboring provinces are (from north clockwise) Mukdahan, Amnat Charoen, Ubon Ratchathani, Sisaket, and Roi Et.
Geography
The northern half of the province consists of plains with low hills; the southern part consists of the river lowlands of the River Chi, with ponds and swamps. Yasothon's total forested area is 358 km2 (138 sq mi) or 8.7% of the province.[2]
Geology
Yasothon soils (rhodic ferralsols) formed in the Triassic before the uplift of the Khorat Plateau, are relict soils made fertile by field termites through bioturbation.[5]
History
The province was created on 1 March 1972, when it was split off from Ubon Ratchathani.
In the past, Yasothon was a fertile land on the banks of the Chi River. Yasothon has a long history associated with Nong Bua Lum Phu Nakhon, Khuean Khan Kab Kaew Bua Ban and related to Ubon City. Around 1771, Phra Chao Ta Chao Phrawo, the old stewards of Vientiane have evacuated their families and dependents to settled and using the name of the new city as "Nong Bua Lum Phu City".
Rattanakosin period
In 1814, King Rama II ordered to raised Ban Singh Tha as a city and gave it the name "Muang Yot Sunthon" and later changed its name to "Yasothon".
During the reign of King Rama III, in the Lao rebellion (1826–1828), Yasothon was enlisted to participate in the victorious battle.
During the reign of King Rama V in 1874, in the Haw wars, Yasothon was enlisted to join forces. Later in 1883, Haw has raised forces to be located at Thung Chiang Kham, Yasothon was enlisted to take the strength of elephants, horses, cows as a vehicle to carry supplies to feed the army.
During the Franco-Siamese War in 1893, French has raised forces to attacked Sombok city, Yasothon was conscripted to help defend the border by bringing troops to join the army from Bangkok.
In 1900 has dissolved the northeastern province, Yasothon has merged with the city of Ubon Ratchathani. It is divided into 2 districts, namely "Uthai Yasothon District" and "Prachim Yasothon District".
In 1913, has changed the name of "Uthai Yasothon District" to "Kham Khuean Kaeo District" and changed the name of "Prachim Yasothon District" to "Yasothon District". Yasothon therefore downgraded from a city to a district since then.
Many years later in 1972, Yasothon was separated from Ubon Ratchathani until present day.
Symbols
The seal of the province shows two mythical lions, called singh, facing the chedi Prathat Anon, in the temple Wat Maha That in the city of Yasothon. In the legendary account of the founding of the city, a lion came out of the forest when the site was chosen; hence the city was called Ban Singh Tha (Thai: บ้านสิงห์ท่า), Home (of) Imposing Lion. At the bottom of the seal is a lotus flower (Nymphaea lotus), as the lotus is both the provincial flower of the province and of Ubon Ratchathani province, of which Yasothon was part until 1972.[6] The provincial tree is Anisoptera costata.
Administrative divisions

Provincial government
The province is divided into nine districts (amphoe). The districts are further subdivided into 78 subdistricts (tambon) and 885 villages (muban).
Local government
As of 26 November 2019 there are:[7] one Yasothon Provincial Administration Organisation (ongkan borihan suan changwat) and 24 municipal (thesaban) areas in the province. Yasothon has town (thesaban mueang) status.[8] Further 23 subdistrict municipalities (thesaban tambon). The non-municipal areas are administered by 63 Subdistrict Administrative Organisations - SAO (ongkan borihan suan tambon).[3]
Transport

Yasothon city is about 500 km (310 mi) from Bangkok at the intersection of Routes 23 and 202, and the south end of Route 2169. Several bus lines connect the province at frequent intervals to Bangkok's Northern Bus Terminal (Thai: หมอชิดใหม่, RTGS: mo chit mai), as well as all bus terminals in the north and northeast. Ubon Ratchathani province is 100 kilometres east on Route 23.
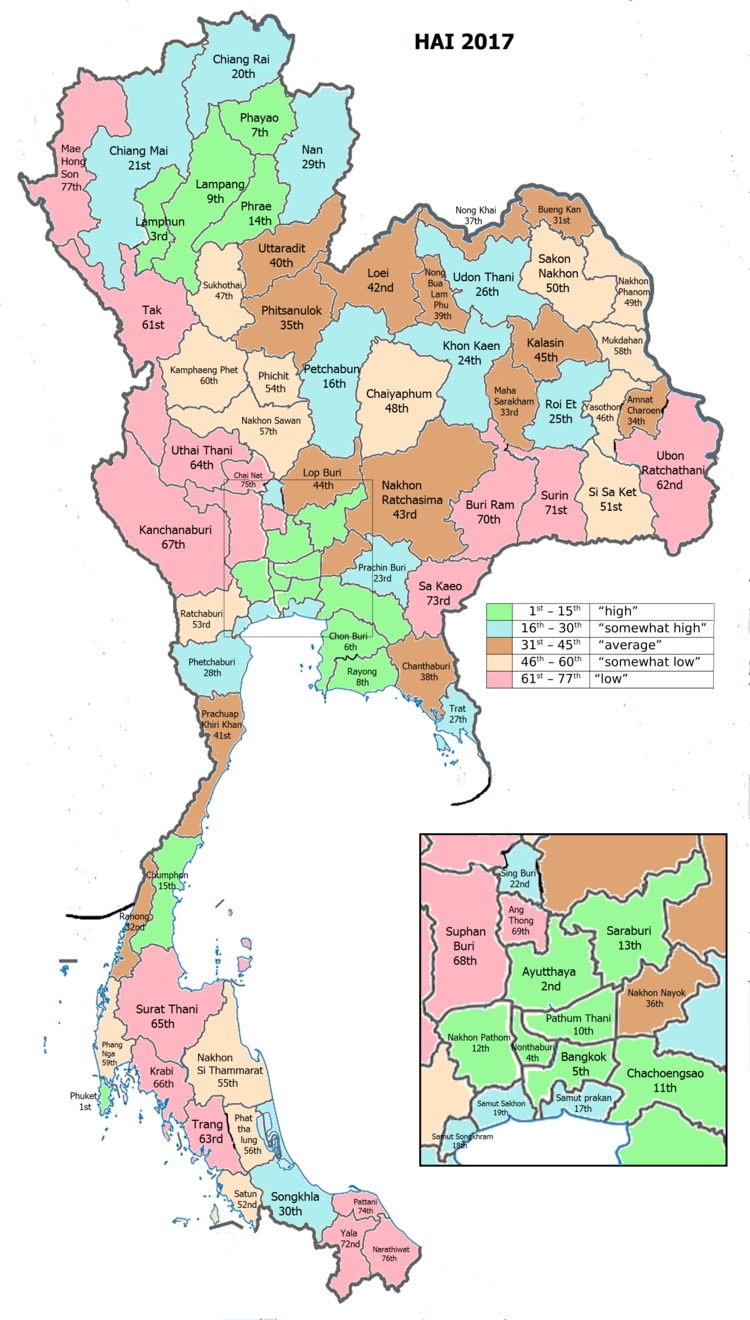
Human achievement index 2017
| Health | Education | Employment | Income |
| 61 | 54 | 14 | 70 |
| Housing | Family | Transport | Participation |
 |
 |
 |
|
| 8 | 23 | 38 | 45 |
| Yasothon, with an HAI 2017 value of 0.5790 is "somewhat low". It ranks 46th of 76 in the ranking. | |||
Since 2003, the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) in Thailand has tracked progress on human development at the provincial level using the Human Achievement Index (HAI), a composite index covering eight key areas of human development. The National Economic and Social Development Board (NESDB) has taken over this task since 2017.[4]
| Rank | Classification |
| 1 - 15 | "high" |
| 16 - 30 | "somewhat high" |
| 31 - 45 | "average" |
| 45 - 60 | "somewhat low" |
| 61 - 77 | "low" |
| Map with provinces and HAI 2017 rankings |
 |
References
- "ประกาศสำนักนายกรัฐมนตรี เรื่อง แต่งตั้งข้าราชการพลเรือนสามัญ" [Announcement of the Prime Minister's Office regarding the appointment of civil servants] (PDF). Royal Thai Government Gazette. 137 (Special 238 Ngor). 20. 9 October 2020. Retrieved 13 April 2021.
- "ตารางที่ 2 พี้นที่ป่าไม้ แยกรายจังหวัด พ.ศ.2562" [Table 2 Forest area Separate province year 2019]. Royal Forest Department (in Thai). 2019. Retrieved 6 April 2021, information, Forest statistics Year 2019, Thailand boundary from Department of Provincial Administration in 2013
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link) - รายงานสถิติจำนวนประชากรและบ้านประจำปี พ.ส.2562 [Statistics, population and house statistics for the year 2019]. Registration Office Department of the Interior, Ministry of the Interior. stat.bora.dopa.go.th (in Thai). 31 December 2019. Archived from the original on 14 June 2019. Retrieved 26 February 2020.
- Human achievement index 2017 by National Economic and Social Development Board (NESDB), pp. 1–40, maps 1–9, retrieved 14 September 2019, ISBN 978-974-9769-33-1
- Lofjle & Kubiniok, Landform development and bioturbation on the Khorat plateau, Northeast Thailand, Nat.Hist.Bull.Siam Soc. (56), 1996 Archived 2011-07-21 at the Wayback Machine[not specific enough to verify]
- "Yasothon". Thailex. Retrieved 12 May 2021.
- "Number of local government organizations by province". dla.go.th. Department of Local Administration (DLA). 26 November 2019. Retrieved 10 December 2019.
46 Yasothon: 1 PAO, 1 Town mun., 23 Subdistrict mun., 63 SAO.
- "พระราชกฤษฎีกา เปลียนแปลงฐานะเทศบาลตำบลยโสธรเป็นเทศบาลเมืองยโสธร พ.ศ.๒๕๓๗" [Royal Decree Re: Change the status of Yasothon Subdistrict Municipality to Yasothon Town Municipality B.E.2537 (1994)] (PDF). Royal Thai Government Gazette. 111 (52 Kor): 46–47. 23 November 1994. Retrieved 10 December 2019.
External links
 Yasothon travel guide from Wikivoyage
Yasothon travel guide from Wikivoyage- Provincial page from the Tourist Authority of Thailand
- Website of province(Thai) Archived 2005-10-01 at the Wayback Machine
На других языках
- [en] Yasothon province
[ru] Ясотхон (провинция)
Ясотхон (тайск. ยโสธร) — провинция на северо-востоке Таиланда, расположена на реке Чи. Граничит с провинциями: Мукдахан, Амнатчарен, Убонратчатани, Сисакет и Ройет.Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии





