world.wikisort.org - Thailand
Trang (Thai: ตรัง, Thai pronunciation: [trāŋ]), also called Mueang Thap Thiang, is one of the southern provinces (changwat) of Thailand, on the west side of the Malay Peninsula facing the Strait of Malacca. Neighboring provinces are (from north clockwise) Krabi, Nakhon Si Thammarat, Phatthalung, and Satun.
Trang
ตรัง | |
|---|---|
Province | |
(Clockwise from top left) Ko Lao Liang Phi in Mu Ko Phetra National Park, Hat Chao Mai National Park at sunset, Dugongs statue at Pak Meng Beach, Tuk-tuk hua kob (frog-headed auto rickshaw) unique vehicle of the province, Railway runs pass Khlong Muan railway halt in the northern part of province, Kantang railway station | |
 Flag  Seal | |
 Map of Thailand highlighting Trang province | |
| Country | Thailand |
| Capital | Trang |
| Government | |
| • Governor | Khajornsak Charoensopha (since October 2020) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 4,918 km2 (1,899 sq mi) |
| • Rank | Ranked 43rd |
| Population (2018)[2] | |
| • Total | 643,116 |
| • Rank | Ranked 41st |
| • Density | 131/km2 (340/sq mi) |
| • Rank | Ranked 34th |
| Human Achievement Index | |
| • HAI (2017) | 0.5530 "low" Ranked 63rd |
| Time zone | UTC+7 (ICT) |
| Postal code | 92xxx |
| Calling code | 075 |
| ISO 3166 code | TH-92 |
| Website | www |
Trang was formerly a port involved in foreign trade. It was the first place where rubber was planted in Thailand. Phraya Ratsadanupradit Mahison Phakdi brought rubber saplings from Malaya and planted them here in 1899, and rubber is now an important export of the country. The Trang River flows through the province from its origin in the Khao Luang mountain range, and the Palian River flows from the Banthat mountains. The province of Trang has an area of approximately 5,000 square km and 199 km of Strait of Malacca shoreline.[4]
Geography
The province is on the coast of the Strait of Malacca, and contains 46 islands together with the mainland area. There are only few plains, and most of the area is hills. The Khao Luang and the Banthat mountain range are the sources of the two main rivers of the province, the Trang River and the Palian River.
The southern coast of the province is protected in the Mu Ko Phetra National Park. The estuary of the Trang River together with the Hat Chao Mai Marine National Park[5] and Ko Libong Non-hunting Area are also registered Ramsar wetlands. The total forest area is 1,093 km2 (422 sq mi) or 23.1 percent of provincial area.[6]
History
Trang was an important seaport in southern Thailand. Legend says that ships always arrived in the morning, which led to the town's name. "Trang" derives from the Malay word for light or dawn (terang). But in another explanation it says that it comes from Sanskrit (tarangque) which means wave or gallop. In addition, the landscape of Trang is characterized by mounds interspersed with plains that look like waves. Thus, the provincial seal features sea waves and a lighthouse bridge.[7]
The province was once a part of the Srivijaya empire, an ancient Hindu-Buddhist Melayu Kingdom and the Malay Sultanate of Kedah until 1810.
According to cultural records Trang was one of 12 satellite towns that existed about 900 years ago, but it was during the reign of King Rama II in 1811 that Trang got its first governor. The first Westerner to arrive in Trang was Captain James Low, who came in 1824 to negotiate commercial benefits.
The original town was in Khuanthani (now a tambon in district Kantang). In 1893, the governor, Phraya Ratsadanupradit Mahison Phakdi, also known as Khaw Sim Bee na Ranong, decided to make Trang an important seaport and relocated the town to Kantang District on the Trang River delta. It was moved again to its present location 26 km inland in 1916 by King Rama VI because of repeated flooding.
Trang was the first area of Thailand where rubber trees were planted, brought there by governor Phraya Ratsadanupradit Mahison Phakdi from British Malaya in 1899.
In 1933, the State Administration was organized, Trang then becomes "Trang province" until the present.
Symbols
The seal of the province shows a lighthouse bridge above a sea of waves. The lighthouse bridge refers to Trang as a seaport trading with foreign countries.[8]
The provincial symbolic flower and tree is the green ebony (Jacaranda filicifolia). The plant was imported from Australia by the same governor who imported the rubber tree, and it quickly got the name "si trang" by the citizens.
Lambchop rasbora (Trigonostigma espei) is a provincial fish.
The provincial slogan เมืองพระยารัษฏา ชาวประชาใจกว้าง ถิ่นกำเนิดยางพารา เด่นสง่าดอกศรีตรัง ปะการังใต้ทะเล เสน่ห์หาดทรายงาม น้ำตกสวยตระการตา translates as "Phraya Rasda's town, generous people, delicious roast pork, the first city where para rubber was planted, the Si Trang provincial flower, underwater coral reefs, scenic beaches and waterfalls."[8]
Administrative divisions

Provincial government
Trang is divided into 10 districts (amphoes). These are further divided into 87 subdistricts (tambons) and 697 villages (mubans).
|
Local government
As of 26 November 2019 there are:[9] one Trang Provincial Administration Organisation (ongkan borihan suan changwat) and 22 municipal (thesaban) areas in the province. Trang has city (thesaban nakhon) status and Kantang has town (thesaban mueang) status. Further 20 subdistrict municipalities (thesaban tambon). The non-municipal areas are administered by 77 Subdistrict Administrative Organisations - SAO (ongkan borihan suan tambon).[2]
Transportation
Air: Trang Airport is 7 km from Trang town centre.[10] It is served by Thailand AirAsia and Nok Air, with flights to Bangkok.
Rail: Trang is one of the southern destinations offering trains to Bangkok railway station. Starting from Thung Song Junction railway station in Nakhon Si Thammarat province, this southwestern route has three stations: Huai Yot railway station at Huai Yot District, Trang railway station and ends at Kantang railway station at Kantang railway station.
Road: Major roads to and from Trang are:
- Highway 4 (Bangkok—Chumphon) via Highway 41 (Surat Thani—Thung Song—Huai Yot—Trang), a distance of 828 kilometres.
- Highway 4 (Bangkok—Chumphon) via Ranong—Phang Nga—Krabi—Trang, a distance of 1,020 kilometres.
- Highway 404-416 (Satun—Palian—Trang), 140 kilometres.
- Highway 4-407 (Hat Yai—Phatthalung—Trang), 148 kilometres.
- Highway 4-402 (Phuket—Phang Nga—Krabi—Trang), 312 kilometres.
Bus:There are buses to and from Trang to Bangkok and main provinces (Phuket, Hat Yai, Krabi, Nakhon Si Thammarat, and Satun).
Boats to islands: Trang has four piers for boats to the islands: Pak Meng Pier, Ban Chao Mai Pier, Klong Son Pier, and Kuan Thung Kuu Pier.
Education
Secondary schools:[citation needed]
- Wichienmatu School วิเชียรมาตุ
- Wichienmatu 2 School วิเชียรมาตุ 2
- Wichienmatu 3 School วิเชียรมาตุ 3
- Saparachinee School สภาราชินี
- Saparachinee 2 School สภาราชินี 2
- Princess Chulabhorn's College,Trang จุฬาภรณ์ราชวิทยาลัย
- Sport School โรงเรียนกีฬาตรัง
- Buranarumluk School บูรณะรำลึก
- Panyawit School ปัญญาวิทย์
- Darunothai School ดรุโณทัย
- Trang vittaya School ตรังวิทยา
- Trangchristiensuksa ตรังคริสเตียนศึกษา
- Wat Kaphang Surin School โรงเรียนวัดกระพังสุรินทร์
- Pornsirikul School พรศิริกุล
- Matayomsuksa Watkuanwisetmulaniti School มัธยมศึกษาวัดควนวิเศษ มูลนิธิ
- Kantangpittayakorn School กันตังพิทยากร
- Kantangratsadasuksa School กันตังรัษฎาศึกษา
- Yantakhao Ratchanupatham School ย่านตาขาวรัฐชนูปถัมภ์
- Palean padungsit School ปะเหลียนผดุงศิษย์
- Kantapittayakarn School คันธพิทยาคาร
- Sikao prachapadungvit School สิเกาประชาผดุงวิทย์
- Wangviset School วังวิเศษ
- Huayyot School ห้วยยอด
- Lampurareungvit School ลำภูราเรืองวิทย์
- Nampud School น้ำผุด
- Ratsada School รัษฎา
- Huaynang ratsadornbamrung School ห้วยนางราษฎรบำรุง
- Ratsadanupradit anusorn School รัษฎานุประดิษย์อนุสรณ์
- Nayong vittayakom School นาโยงวิทยาคม
- Sawatratanapimuk School สวัสดิ์รัตนาภิมุข
- Thungnonghang prachason School ทุ่งหนองแห้งประชาสรรค์
- Hatsumran vittayakom School หาดสำราญวิทยาคม
- Trang polytechnic School ตรังโปลีเทคนิค
Higher education:
- Rajamangala University of Technology Srivijaya (Trang campus)
- Prince of Songkla University (Trang campus)
- Ramkhamhaeng University (Trang campus)
- Suan Dusit Rajabhat University (Trang center)
- Boromrajonane College of Nursing
- Sirindhorn College of Public Health
- Trang Technical College
- Trang College of Agricultural and Technology
- Trang Polytechnic College
- Siam Commercial College
Healthcare
- Trang Hospital (main hospital, public)
- Watanapat Hospital (private)
- Trang Ruampat Hospital (private)
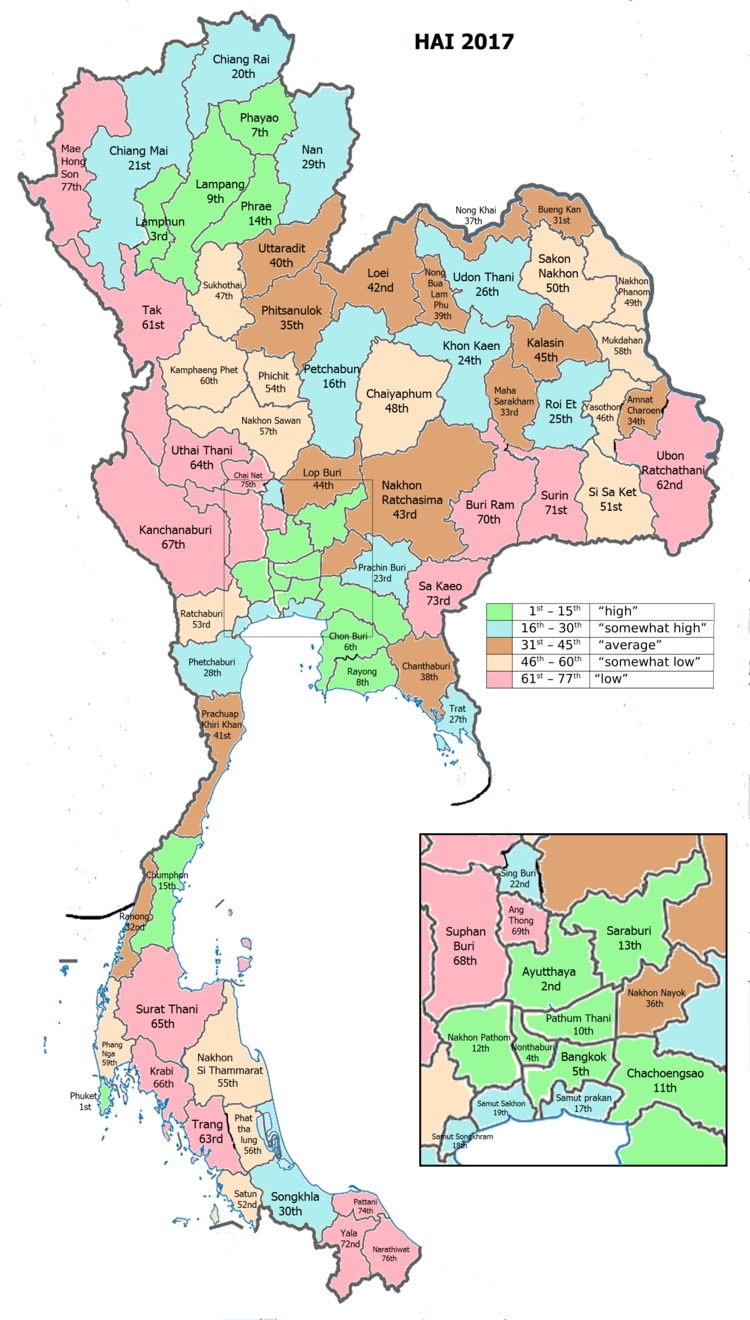
Human achievement index 2017
| Health | Education | Employment | Income |
| 57 | 36 | 62 | 59 |
| Housing | Family | Transport | Participation |
 |
 |
 |
|
| 63 | 56 | 13 | 54 |
| Province Trang, with an HAI 2017 value of 0.5530 is "low", occupies place 63 in the ranking. | |||
Since 2003, United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) in Thailand has tracked progress on human development at sub-national level using the Human achievement index (HAI), a composite index covering all the eight key areas of human development. National Economic and Social Development Board (NESDB) has taken over this task since 2017.[3]
| Rank | Classification |
| 1 - 15 | "high" |
| 16 - 30 | "somewhat high" |
| 31 - 45 | "average" |
| 45 - 60 | "somewhat low" |
| 61 - 77 | "low" |
| Map with provinces and HAI 2017 rankings |
 |
Events and festivals
- Trang Vegetarian Festival (เทศกาลกินเจ): since Trang has a large population of Thai-Chinese, therefore causing the Vegetarian Festival in October annually alike to Phuket. People become vegetarian and dress in white for nine days and nights. This should bring them good fortune. Trang is one of the provinces that hold this festival superbly.[11]
- Trang Underwater Wedding Ceremony (พิธีวิวาห์ใต้สมุทร): is a wedding ceremony under the sea of Trang. It was first held in early 1996, and ever since, it has been continuously held every year during the Valentine's Festival. This ceremony is promoted by the Tourism Authority of Thailand (TAT).[12]
- Marine Pulling Buddha Procession (ชักพระทางทะเล): or Chak Phra in Thai is a Buddhist festival that is generally performed in many provinces of the southern such as Surat Thani. Chakra Phra is to invite Buddha image into a boat and paddle to various places on the water for prosperity. But Trang is the only province that holds this festival by sea. Chak Phra is held annually after the end of Buddhist Lent (during October).[13]
Local food
Trang is another province rich with famous local food even receiving the nickname "The Land of Food" for example[14]
- Mu yang (หมูย่าง), also known as Mu han (หมูหัน): a barbecue roasted piglet with crispy skin, regarded as a menu that has been influenced by Cantonese cuisine for over 100 years.[15]
- Dim sum: Trang regarded as a province where has a unique breakfast cuisine found nowhere else in Thailand. There are many coffee shops in the form of Kopi tiam (traditional coffee shop) that served in a variety of menus such as Pathongko (Youtiao), Khanom jeeb (Shumai), Har gow (white shrimp dumpling), Salapao (Siopao), Popia thot (deep fried spring roll) include Mu yang.
- Trang cake, also known as Kook Ming cake: a traditional cake that originated in Lamphu Ra, 14 km north of Mueang Trang. These cakes were cooked by an authentic process by baking in the charcoal oven and have no frosting with have several flavours like orange, coffee, pandan, three-flavoured etc.[14]
Gallery
- Rajamangala Beach
- Trees at Rajamangala Beach, Trang coastline
- Mu Ko Phetra National Park
- Another corner of Mu Ko Phetra National Park
- View of Mai Fat, the sub-district of Sikao
- Silhouette of Pak Meng Beach, a part of Hat Chao Mai National Park and most renowned beach of the province
- Clear water and long-tailed boat at Ko Kradan
- Sunset at Ko Muk
References
- Advancing Human Development through the ASEAN Community, Thailand Human Development Report 2014, table 0:Basic Data (PDF) (Report). United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) Thailand. pp. 134–135. ISBN 978-974-680-368-7. Retrieved 17 January 2016, Data has been supplied by Land Development Department, Ministry of Agriculture and Cooperatives, at Wayback Machine.
{{cite report}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link)[dead link] - "รายงานสถิติจำนวนประชากรและบ้านประจำปี พ.ศ.2561" [Statistics, population and house statistics for the year 2018]. Registration Office Department of the Interior, Ministry of the Interior (in Thai). 31 December 2018. Retrieved 20 June 2019.
- Human achievement index 2017 by National Economic and Social Development Board (NESDB), pages 1-40, maps 1-9, retrieved 14 September 2019, ISBN 978-974-9769-33-1
- "Trang". Tourism Authority of Thailand (TAT). Archived from the original on 19 June 2012. Retrieved 18 May 2015.
- "Hat Chao Mai National Park". Department of National Parks (DNP) Thailand. Archived from the original on 24 May 2015. Retrieved 24 May 2015.
- "ตารางที่ 2 พี้นที่ป่าไม้ แยกรายจังหวัด พ.ศ.2562" [Table 2 Forest area Separate province year 2019]. Royal Forest Department (in Thai). 2019. Retrieved 6 April 2021, information, Forest statistics Year 2019
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: postscript (link) - Jaisamut, Yuenyad (1996). ตรัง : เมืองท่าโบราณสองพันปี นายกรัฐมนตรีสองยุค [Trang: Two Thousand Years Ancient Seaport, Two Periods Prime Minister] (in Thai). Bangkok: Matichon. pp. 47–50. ISBN 9747115603.
- "Symbol of Trang". OSM Andamnan: The Office of Strategy Management for Southern Province Cluster. Retrieved 26 May 2015.
- "Number of local government organizations by province". dla.go.th. Department of Local Administration (DLA). 26 November 2019. Retrieved 10 December 2019.
14 Trang: 1 PAO, 1 City mun., 1 Town mun., 20 Subdistrict mun., 77 SAO.
- "Trang Airport". Department of Civil Aviation (DCA): Trang. Archived from the original on 24 May 2015. Retrieved 24 May 2015.
- "Top 5 provinces to visit for vegetarian festival". Bangkok Post. 2017-08-16. Retrieved 2020-03-01.
- "Trang Underwater Wedding Ceremony 2019". Thailand Festival.
- Archived at Ghostarchive and the Wayback Machine: Channel 9 MCOT HD (2019-10-20). "ชักพระทางน้ำข้ามทะเลหลังออกพรรษา จ.ตรัง" [Pulling Buddha across the sea after Buddhist Lent, Trang province]. youtube (in Thai). Retrieved 2020-03-02.
- Tamkarnwela (2015-08-24). "~ * ~ * ~ * Let's Enjoy Eating @Trang Province...The Land of Food Paradise & Deliciousness... of More than 40 Restaurants ~ * ~ * ~* ~". READE.ME. Retrieved 2020-04-19.
- Mueangkaeo, Methee (2018-10-16). "'หมูย่างเมืองตรัง' อร่อยล้ำกว่า 100 ปี" ['Trang Roasted Pork' tasty over 100 years]. Posttoday (in Thai). Retrieved 2020-04-19.
External links
 Trang travel guide from Wikivoyage
Trang travel guide from Wikivoyage- Provincial website
На других языках
[de] Trang (Provinz)
Trang (Thai ตรัง) ist eine Provinz (Changwat) in der Südregion von Thailand. Die Hauptstadt der Provinz heißt ebenfalls Trang.- [en] Trang province
[ru] Транг (провинция)
Транг (тайск. ตรัง) — провинция на юге Таиланда, расположена на западном побережье полуострова Малакка. Граничит с провинциями: Краби, Накхонситхаммарат, Пхаттхалунг и Сатун.Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии













