world.wikisort.org - Philippines
Parang, officially the Municipality of Parang (Maguindanaon: Inged nu Parang, Jawi: ايڠايد نو ڤارڠ; Iranun: Inged a Parang, ايڠايد ا ڤارڠ; Tagalog: Bayan ng Parang), is a 1st class municipality in the province of Maguindanao del Norte, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 102,914 people. [3]
Parang | |
|---|---|
Municipality | |
| Municipality of Parang | |
 Polloc Port | |
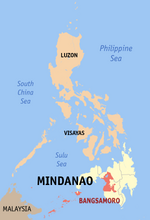
 Map of Maguindanao del Norte with Parang highlighted | |
OpenStreetMap  | |
 Parang Location within the Philippines | |
| Coordinates: 7°22′28″N 124°16′07″E | |
| Country | Philippines |
| Region | Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao |
| Province | Maguindanao del Norte |
| District | Lone district |
| Founded | August 18, 1947 |
| Barangays | 25 (see Barangays) |
| Government | |
| • Type | Sangguniang Bayan |
| • Mayor | Cahar P. Ibay |
| • Vice Mayor | Adnan C. Biruar |
| • Representative | Sittie Shahara "Dimple" I. Mastura |
| • Municipal Council | Members |
| • Electorate | 54,873 voters (2022) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 850.78 km2 (328.49 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 57 m (187 ft) |
| Highest elevation | 366 m (1,201 ft) |
| Lowest elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 102,914 |
| • Density | 120/km2 (310/sq mi) |
| • Households | 17,712 |
| Economy | |
| • Income class | 1st municipal income class |
| • Poverty incidence | 49.06% (2018)[4] |
| • Revenue | ₱384,792,000.00 (2020) |
| • Assets | ₱135,747,000.00 (2020) |
| • Expenditure | ₱382,818,000.00 (2020) |
| • Liabilities | ₱2,364,000.00 (2020) |
| Service provider | |
| • Electricity | Maguindanao Electric Cooperative (MAGELCO) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (PST) |
| ZIP code | 9604 |
| PSGC | |
| IDD : area code | +63 (0)64 |
| Native languages | Maguindanao Iranun Tagalog |
| Website | http://www.lgu-parang.gov.ph/ |
The town was part of the province of Shariff Kabunsuan from October 2006 until its nullification by the Supreme Court in July 2008.
History
The history of Parang traces back to the era when it used to be an integral part of the Maguindanao Sultanate. In June 1851, the Spanish military government based in Zamboanga sent forces to Polloc, presently a barangay of Parang, and seized it.[5] Having a natural deep water harbor, the Spanish then set up a fortress and a naval base at Polloc,[6] from which they would launch military operations against the Moros of the Pulangui Valley.
Polloc eventually grew into a small town that by 1860 it was home to 600 Christians and 50-60 Chinese traders along with people from other walks of life.[7] In 1884, a road was built between Polloc and the other town of Cotabato, which was founded ten years later than Polloc in 1861 and now served as the capital of the 5th Military District of Cotabato in which Polloc was part of.
The Americans took over local affairs when the Spanish evacuated at the aftermath of the Philippine-American War in 1901 and the American authorities replaced them. When political reorganization of the Philippine islands took place in 1917, Polloc was made part of the newly created municipal district of Parang.[8] Parang as a municipality was created on August 18, 1947, through Executive Order No. 82 signed by President Manuel Roxas.[9] The modern Polloc Port, which form the main part of the present-day Polloc Freeport and Economic Zone currently based in Barangay Polloc of Parang town, was constructed in 1977 and currently serves as the primary transshipment port in the Bangsamoro region.[10]
Geography
It is bordered to the north by Barira and Matanog, on the east by Buldon, and on the south is Sultan Kudarat.
Barangays
Parang is politically subdivided into 25 barangays.
- Bongo Island (Litayen)
- Campo Islam
- Cotongan
- Datu Macarimbang Biruar
- Gadungan
- Gadungan Pedpandaran
- Guiday T. Biruar
- Gumagadong Calawag
- Kabuan
- Landasan (Sarmiento)
- Limbayan
- Macasandag
- Magsaysay
- Making
- Manion
- Moro Point
- Nituan
- Orandang
- Pinantao
- Poblacion
- Poblacion II
- Polloc
- Samberen
- Tagudtongan
- Tuca-Maror
Climate
| Climate data for Parang, Maguindanao | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 28 (82) |
28 (82) |
29 (84) |
29 (84) |
27 (81) |
26 (79) |
26 (79) |
26 (79) |
27 (81) |
26 (79) |
27 (81) |
27 (81) |
27 (81) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 19 (66) |
19 (66) |
19 (66) |
20 (68) |
21 (70) |
20 (68) |
20 (68) |
20 (68) |
20 (68) |
20 (68) |
20 (68) |
19 (66) |
20 (68) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 53 (2.1) |
44 (1.7) |
41 (1.6) |
39 (1.5) |
69 (2.7) |
89 (3.5) |
92 (3.6) |
97 (3.8) |
72 (2.8) |
79 (3.1) |
72 (2.8) |
49 (1.9) |
796 (31.1) |
| Average rainy days | 15.3 | 13.5 | 16.3 | 16.9 | 22.3 | 23.5 | 22.5 | 23.1 | 19.4 | 21.5 | 20.6 | 17.5 | 232.4 |
| Source: Meteoblue (modeled/calculated data, not measured locally)[11] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
|---|---|---|
| 1903 | 603 | — |
| 1918 | 1,933 | +8.08% |
| 1939 | 4,495 | +4.10% |
| 1948 | 13,413 | +12.92% |
| 1960 | 37,296 | +8.89% |
| 1970 | 31,667 | −1.62% |
| 1975 | 32,506 | +0.53% |
| 1980 | 46,003 | +7.19% |
| 1990 | 55,355 | +1.87% |
| 1995 | 49,562 | −2.05% |
| 2000 | 60,935 | +4.53% |
| 2007 | 102,247 | +7.40% |
| 2010 | 73,328 | −11.40% |
| 2015 | 89,194 | +3.80% |
| 2020 | 102,914 | +2.85% |
| Source: Philippine Statistics Authority [12] [13] [14][15] | ||
Economy
Tourism
A cultural festival is held every August 18 in commemoration of the founding anniversary of Parang. Events are organized by the municipal government with the participation of various stakeholders
Tourist attractions in Parang include:
- Golf course in Camp S.K Pendatun
- Zone Beach
- Punta Beach
- White Sand Beach in Limbayan, Bonggo Island
- Molina-Munoz Farm Resort
- Fruit Bats Sanctuary
- Bacolod street
- Simento white camp
Infrastructure
Transportation
Major sea cargo vessels connect Polloc Port to Manila and other Philippine cities.
Tricycles are the main modes of public transport in the municipality. Several shuttle vans and PUJs provide regular trips to Cotabato City and other municipalities.
Health
- 1 District Hospital
- 1 Rural Health Unit
- 1 Private Hospital
- 1 Medical/Dental Hospital(PNP)
- 1 Medical Diagnostic Laboratory
Utilities
Magelco (Maguindanao Electric Cooperative, Inc.) provides electric power to the locality. Inland barangays use solar power as installed by our donor agencies.
Education
- Tertiary: 3 private schools
- Secondary: 5 public schools;3 private schools
- Elementary: 14 public schools;4 private schools
- Primary: 14 public schools
- Pre-School: 2 public schools;5 private schools
Sister Cities
 Cotabato City, Philippines
Cotabato City, Philippines
References
- Municipality of Parang | (DILG)
- "2015 Census of Population, Report No. 3 – Population, Land Area, and Population Density" (PDF). Philippine Statistics Authority. Quezon City, Philippines. August 2016. ISSN 0117-1453. Archived (PDF) from the original on May 25, 2021. Retrieved July 16, 2021.
- Census of Population (2020). "BARMM". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. PSA. Retrieved 8 July 2021.
- "PSA Releases the 2018 Municipal and City Level Poverty Estimates". Philippine Statistics Authority. 15 December 2021. Retrieved 22 January 2022.
- Census Office, Philippines (1920). "Census of the Philippine Islands Taken Under the Direction of the Philippine Legislature in the Year 1918, Volume 1". p. 149. Retrieved 13 October 2021.
- P.J. Westler (1922). "Mindanao and the Sulu Archipelago: Their Natural Resources and Opportunities for Development". p. 41. Retrieved 13 October 2021.
- Jose S. Arcilla. "The Return of the Jesuits to Mindanao". p. 24. Retrieved 13 October 2021.
- "Act No. 2711". Retrieved 13 October 2021.
- "Executive Order No. 82, s. 1847". Retrieved 26 August 2021.
- "Polloc Freeport and Ecozone - BARMM". Retrieved 26 August 2021.
- "Parang, Maguindanao : Average Temperatures and Rainfall". Meteoblue. Retrieved 19 January 2019.
- Census of Population (2015). "ARMM – Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. PSA. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- Census of Population and Housing (2010). "ARMM – Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. NSO. Retrieved 29 June 2016.
- Censuses of Population (1903–2007). "ARMM – Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao". Table 1. Population Enumerated in Various Censuses by Province/Highly Urbanized City: 1903 to 2007. NSO.
- "Province of Maguindanao". Municipality Population Data. Local Water Utilities Administration Research Division. Retrieved 17 December 2016.
- "Poverty incidence (PI):". Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 28 December 2020.
- https://psa.gov.ph/sites/default/files/NSCB_LocalPovertyPhilippines_0.pdf; publication date: 29 November 2005; publisher: Philippine Statistics Authority.
- https://psa.gov.ph/sites/default/files/2003%20SAE%20of%20poverty%20%28Full%20Report%29_1.pdf; publication date: 23 March 2009; publisher: Philippine Statistics Authority.
- https://psa.gov.ph/sites/default/files/2006%20and%202009%20City%20and%20Municipal%20Level%20Poverty%20Estimates_0_1.pdf; publication date: 3 August 2012; publisher: Philippine Statistics Authority.
- https://psa.gov.ph/sites/default/files/2012%20Municipal%20and%20City%20Level%20Poverty%20Estima7tes%20Publication%20%281%29.pdf; publication date: 31 May 2016; publisher: Philippine Statistics Authority.
- https://psa.gov.ph/sites/default/files/City%20and%20Municipal-level%20Small%20Area%20Poverty%20Estimates_%202009%2C%202012%20and%202015_0.xlsx; publication date: 10 July 2019; publisher: Philippine Statistics Authority.
- "PSA Releases the 2018 Municipal and City Level Poverty Estimates". Philippine Statistics Authority. 15 December 2021. Retrieved 22 January 2022.
External links
- Parang Profile at the DTI Cities and Municipalities Competitive Index
- Philippine Standard Geographic Code
- Philippine Census Information
- Local Governance Performance Management System
На других языках
[de] Parang (Maguindanao)
Parang ist eine philippinische Stadtgemeinde in der Provinz Maguindanao. Sie hat 89.194 Einwohner (Zensus 1. August 2015).- [en] Parang, Maguindanao del Norte
Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии