world.wikisort.org - Philippines
Tangub, officially known as the City of Tangub (Cebuano: Dakbayan sa Tangub; Tagalog: Lungsod ng Tangub), is a 4th class component city in the province of Misamis Occidental, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 68,389 people. [3]
Tangub
Regidor | |
|---|---|
Component city | |
| City of Tangub | |
 Tangub City Sports Complex | |
 Seal | |
| Nickname: Christmas Symbols Capital of the Philippines | |
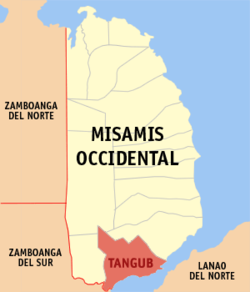 Map of Misamis Occidental with Tangub highlighted | |
OpenStreetMap  | |
 Tangub Location within the Philippines | |
| Coordinates: 8°04′00″N 123°45′00″E | |
| Country | Philippines |
| Region | Northern Mindanao |
| Province | Misamis Occidental |
| District | 2nd district |
| Founded | December 4, 1929 |
| Cityhood | June 17, 1967 |
| Barangays | 55 (see Barangays) |
| Government | |
| • Type | Sangguniang Panlungsod |
| • Mayor | Sabiniano "Ben" S. Canama (NP) |
| • Vice Mayor | Tito B. Decina (PDPLBN) |
| • Representative | Sancho Fernando "Ando" F. Oaminal (NP) |
| • City Council | Members |
| • Electorate | 40,080 voters (2019) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 162.78 km2 (62.85 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 243 m (797 ft) |
| Highest elevation | 2,421 m (7,943 ft) |
| Lowest elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 68,389 |
| • Density | 420/km2 (1,100/sq mi) |
| • Households | 12,868 |
| Economy | |
| • Income class | 4th city income class |
| • Poverty incidence | 27.50% (2018)[4] |
| • Revenue | ₱651,952,141.00 (2020) |
| • Assets | ₱1,846,288,261.00 (2020) |
| • Expenditure | ₱435,133,395.00 (2020) |
| • Liabilities | ₱487,197,670.00 (2020) |
| Service provider | |
| • Electricity | Misamis Occidental 2 Electric Cooperative (MOELCI 2) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (PST) |
| ZIP code | 7214 |
| PSGC | |
| IDD : area code | +63 (0)88 |
| Native languages | Subanon Cebuano Tagalog |
| Feast date | September 29 |
| Catholic diocese | Archdiocese of Ozamiz |
| Patron saint | Michael the Archangel |
| Website | tangubcity |
Tangub City is also where the Panguil Bay Bridge is situated. Once completed, the 3.77 km (2.34 mi) bridge will connect Tangub, Misamis Occidental to Tubod, Lanao del Norte.
History
The city of Tangub grew from a small town. The cty's name came from the Subanen word "Tangkub", which is a rice container made of tree bark woven together by rattan strips. A Spanish soldier on patrol in the area found a dead man whom the Subanens described as bitten by a snake inside the “tangkub” when he checked if there was still rice in the container. Not understanding the dialect, the soldiers reported that there was a dead man from “tangkub” and the name stuck, which later on was changed to Tangub.
Trade and commerce emerged when many agricultural products were harvested, and the Subanos bartered their land for goods brought in by other Christian settlers. Years after, Chinese merchants settled in this place and helped to hasten the transportation of the settlements into a civilized communities. Tangub became successful during the years 1898-1910. In 1929, Tangub became a municipality by virtue of an executive order by American Governor-General Dwight Davis. In this process, Tangub was separated from its mother municipality of Misamis, now Ozamiz City. The new municipality of Tangub then included all the barrios of the present municipality of Bonifacio, formerly known as Digson. Bonifacio became a municipality, shortly before the outbreak of the Second World War with Hon. Demetrio Fernan as municipal mayor. At some point, the name of the municipality was changed to “Regidor”; however it was reverted a few years later.
Cityhood
On June 17, 1967, under Republic Act No. 5131, Tangub became a chartered city.
Geography
Tangub is close to Zamboanga del Sur and Zamboanga del Norte provinces, while across the bay is Lanao del Norte. Tangub is 77.1 km (77,100 mi) from Maria Cristina Falls, the main source of hydroelectric power in Mindanao.
Climate
| Climate data for Tangub City, Misamis Occidental | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 29 (84) |
30 (86) |
31 (88) |
31 (88) |
30 (86) |
30 (86) |
29 (84) |
30 (86) |
30 (86) |
30 (86) |
30 (86) |
30 (86) |
30 (86) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 22 (72) |
22 (72) |
22 (72) |
23 (73) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
23 (73) |
23 (73) |
23 (74) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 69 (2.7) |
58 (2.3) |
67 (2.6) |
60 (2.4) |
109 (4.3) |
114 (4.5) |
83 (3.3) |
78 (3.1) |
76 (3.0) |
92 (3.6) |
86 (3.4) |
63 (2.5) |
955 (37.7) |
| Average rainy days | 12.8 | 11.6 | 14.8 | 17.4 | 24.8 | 23.5 | 20.7 | 18.5 | 17.4 | 22.5 | 21.6 | 15.6 | 221.2 |
| Source: Meteoblue[5] | |||||||||||||
Barangays
Tangub is politically subdivided into 55 barangays.
- Silanga
- Marcos (Aquino)
- Santa Maria (Baga)
- Balatacan
- Baluk
- Banglay
- Mantic
- Mingcanaway
- Bintana
- Bocator
- Bongabong
- Caniangan
- Capalaran
- Catagan
- Barangay I - City Hall (Poblacion)
- Barangay II - Marilou Annex (Poblacion)
- Barangay IV - St. Michael (Poblacion)
- Isidro D. Tan (Dimalooc)
- Garang
- Guinabot
- Guinalaban
- Hoyohoy
- Kauswagan
- Kimat
- Labuyo
- Lorenzo Tan
- Barangay VI - Lower Polao (Poblacion)
- Lumban
- Maloro
- Barangay V - Malubog (Poblacion)
- Manga
- Maquilao
- Barangay III- Market Kalubian (Poblacion)
- Matugnao
- Minsubong
- Owayan
- Paiton
- Panalsalan
- Pangabuan
- Prenza
- Salimpuno
- San Antonio
- San Apolinario
- San Vicente
- Santa Cruz
- Santo Niño
- Sicot
- Silanga
- Silangit
- Simasay
- Sumirap
- Taguite
- Tituron
- Tugas
- Barangay VII - Upper Polao (Poblacion)
- Villaba
Demographics
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
|---|---|---|
| 1939 | 44,743 | — |
| 1948 | 20,353 | −8.38% |
| 1960 | 21,101 | +0.30% |
| 1970 | 30,918 | +3.89% |
| 1975 | 40,461 | +5.54% |
| 1980 | 40,401 | −0.03% |
| 1990 | 42,926 | +0.61% |
| 1995 | 46,004 | +1.31% |
| 2000 | 49,695 | +1.67% |
| 2007 | 56,644 | +1.82% |
| 2010 | 59,892 | +2.05% |
| 2015 | 63,011 | +0.97% |
| 2020 | 68,389 | +1.62% |
| Source: Philippine Statistics Authority [6] [7] [8][9] | ||
In the 2020 census, the population of Tangub was 68,389 people, [3] with a density of 420 inhabitants per square kilometre or 1,100 inhabitants per square mile.
Economy
Culture
Notable events and festivals
Tangub, through its Sinanduloy Cultural Troupe, is a regular participant of the Sinulog Festival, a festival held in Cebu City. This festival is the pageantry of sights, sounds and colors as it honors and pays homage to Sr. Santo Niño, the child Jesus. The highlights of the festival is from January 9–18, yearly. Tangub City has won a record of twelve grand champion streak in the Sinulog-Based Category of the festival.
Through the recent years, Tangub has been popularly dubbed as the Christmas Symbols Capital of the Philippines. Every year, the city will celebrate Christmas through the Tangub City Christmas Symbols Festival. During the month-long festival, the city fills with a delightful array of illuminated holiday decor, bathing the streets in a most enticing glow.
The city also has a festival called the Dalit Cultural Festivial. It is held in honor of the city's patron saint, Saint Michael the Archangel. It is celebrated every September 29-the feast day of Michaelmas. It is participated by the city's barangays through clusters represented by local schools.
The Harvest Festival showcases various agricultural products for selling and promotion. The festival is a venue to promote the agri-tourism program of the city, creating business-matching opportunities for the people of Tangub City.
Tourism
- Hoyohoy Highland Stone Chapel Adventure Park, is a nature park located on the outskirts of the city, on the foot of Mount Malindang. The park provides a good view of Tangub and the Panguil Bay. Located 850 meters (2788.71 ft) above sea level, the park has a stone chapel, an organic herbal garden, a zipline which is said to be the longest in Asia which connects hills to mountains, and an agricultural learning institute.
- Memorial Hill, is a small hill located inside the prison reservation compound. This place is a crowd favorite not only because of its breathtaking scenery but also because of its historical significance. This hill has a World War II Vintage Japanese canon. It is also a burial site of Eriberto B. Misa Jr, the famous Prison’s Director from years 1937 to 1949.
Sister cities
 Parañaque, Philippines
Parañaque, Philippines Ozamiz, Philippines
Ozamiz, Philippines
See also
- List of renamed cities and municipalities in the Philippines
References
- City of Tangub | (DILG)
- "2015 Census of Population, Report No. 3 – Population, Land Area, and Population Density" (PDF). Philippine Statistics Authority. Quezon City, Philippines. August 2016. ISSN 0117-1453. Archived (PDF) from the original on May 25, 2021. Retrieved July 16, 2021.
- Census of Population (2020). "Region X (Northern Mindanao)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. PSA. Retrieved July 8, 2021.
- "PSA Releases the 2018 Municipal and City Level Poverty Estimates". Philippine Statistics Authority. December 15, 2021. Retrieved January 22, 2022.
- "Tangub: Average Temperatures and Rainfall". Meteoblue. Retrieved April 29, 2020.
- Census of Population (2015). "Region X (Northern Mindanao)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. PSA. Retrieved June 20, 2016.
- Census of Population and Housing (2010). "Region X (Northern Mindanao)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. NSO. Retrieved June 29, 2016.
- Censuses of Population (1903–2007). "Region X (Northern Mindanao)". Table 1. Population Enumerated in Various Censuses by Province/Highly Urbanized City: 1903 to 2007. NSO.
- "Province of Misamis Occidental". Municipality Population Data. Local Water Utilities Administration Research Division. Retrieved December 17, 2016.
- "Poverty incidence (PI):". Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved December 28, 2020.
- https://psa.gov.ph/sites/default/files/NSCB_LocalPovertyPhilippines_0.pdf; publication date: 29 November 2005; publisher: Philippine Statistics Authority.
- https://psa.gov.ph/sites/default/files/2003%20SAE%20of%20poverty%20%28Full%20Report%29_1.pdf; publication date: 23 March 2009; publisher: Philippine Statistics Authority.
- https://psa.gov.ph/sites/default/files/2006%20and%202009%20City%20and%20Municipal%20Level%20Poverty%20Estimates_0_1.pdf; publication date: 3 August 2012; publisher: Philippine Statistics Authority.
- https://psa.gov.ph/sites/default/files/2012%20Municipal%20and%20City%20Level%20Poverty%20Estima7tes%20Publication%20%281%29.pdf; publication date: 31 May 2016; publisher: Philippine Statistics Authority.
- https://psa.gov.ph/sites/default/files/City%20and%20Municipal-level%20Small%20Area%20Poverty%20Estimates_%202009%2C%202012%20and%202015_0.xlsx; publication date: 10 July 2019; publisher: Philippine Statistics Authority.
- "PSA Releases the 2018 Municipal and City Level Poverty Estimates". Philippine Statistics Authority. December 15, 2021. Retrieved January 22, 2022.
External links
- Philippine Standard Geographic Code
- Philippine Census Information
- Local Governance Performance Management System
На других языках
[de] Tangub City
Tangub City ist eine der Stadt und liegt auf der Insel Mindanao in der philippinischen Provinz Misamis Occidental.- [en] Tangub
Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии