world.wikisort.org - India
Haryana (/hʌriˈɑːnə/; Hindi: [ɦəɾɪˈjɑːɳɑː]) is an Indian state located in the northern part of the country. It was carved out of the former state of East Punjab on 1 November 1966 on a linguistic basis. It is ranked 21st in terms of area, with less than 1.4% (44,212 km2 or 17,070 sq mi) of India's land area.[1][12] The state capital is Chandigarh, which it shares with the neighboring state of Punjab, and the most populous city is Faridabad, which is a part of the National Capital Region. The city of Gurugram is among India's largest financial and technology hubs.[13] Haryana has 6 administrative divisions, 22 districts, 72 sub-divisions, 93 revenue tehsils, 50 sub-tehsils, 140 community development blocks, 154 cities and towns, 7,356 villages, and 6,222 villages panchayats.[12][14]
Haryana | |
|---|---|
State | |
|
From top, left to right: Cyber City, Gurugram, Pinjore Gardens, bronze chariot of Krishna and Arjuna at Kurukshetra, Asigarh Fort, Sheikh Chilli's Tomb, Lake in Surajkund. | |
 Seal | |
 Location of Haryana in India | |
| Coordinates (Chandigarh): 30°44′N 76°47′E | |
| Country | |
| Statehood | 1 November 1966 |
| Capital | Chandigarh† |
| Largest city | Faridabad |
| Smart cities | Karnal and Faridabad |
| Districts | 22 |
| Government | |
| • Body | Government of Haryana |
| • Governor | Bandaru Dattatreya |
| • Chief Minister | Manohar Lal Khattar (BJP) |
| • Legislature | Unicameral
|
| • Parliamentary constituency | Rajya Sabha (5 seats) Lok Sabha (10 seats) |
| • High Court | Punjab and Haryana High Court |
| Area | |
| • Total | 44,212 km2 (17,070 sq mi) |
| • Rank | 21st |
| Population (2011) | |
| • Total | 25,351,462 |
| • Rank | 18th |
| • Density | 573/km2 (1,480/sq mi) |
| • Rank | 10 |
| Demonym | Haryanvi |
| Languages[2][3] | |
| • Official | Hindi |
| • Additional official | |
| • Regional | [4][5][6][7][8] |
| GSDP (2020–21) | |
| • Total | ₹7.65 trillion (US$96 billion) |
| • Per capita | ₹239,535 (US$3,000) |
| Time zone | UTC+05:30 (IST) |
| ISO 3166 code | IN-HR |
| Vehicle registration | HR-xx |
| HDI (2019) | |
| HDI rank | 12th |
| Sex ratio | 0.910♀/♂[11] |
| Literacy | 83.78% |
| Website | haryana |
| Symbols of Haryana | |
| Emblem | Emblem of Haryana |
| Mammal | |
| Bird |  |
| Flower | |
| Tree | |
| ^† Joint Capital with Punjab †† Common for Punjab, Haryana and Chandigarh. | |
Haryana contains 32 special economic zones (SEZs), mainly located within the industrial corridor projects connecting the National Capital Region.[12][15] Gurgaon is considered one of the major information technology and automobile hubs of India.[16][17] Haryana ranks 11th among Indian states in human development index.[10] The economy of Haryana is the 13th largest in India, with a gross state domestic product (GSDP) of ₹7.65 trillion (US$96 billion) and has the country's 5th-highest GSDP per capita of ₹240,000 (US$3,000).[9] Haryana has the highest unemployment rate among Indian states.[18]
The state is rich in history, monuments, heritage, flora and fauna and tourism, with a well developed economy, national highways and state roads. It is bordered by Punjab and Himachal Pradesh to the north, by Rajasthan to the west and south, while river Yamuna forms its eastern border with Uttar Pradesh. Haryana surrounds the country's capital territory of Delhi on three sides (north, west and south), consequently a large area of Haryana state is included in the economically important National Capital Region of India for the purposes of planning and development.
Etymology
Anthropologists came up with the view that Haryana was known by this name because in the post- Mahabharata period here lived the Abhiras[19] who developed special skills in the art of agriculture.[20] According to Pran Nath Chopra Haryana got its name from Abhirayana-Ahirayana-Hirayana-Haryana.[21]
History
Ancient period
The villages of Rakhigarhi in Hisar district and Bhirrana in Fatehabad district are home to the largest and one of the world's oldest ancient Indus Valley Civilization sites, dated at over 9,000 years old. Evidence of paved roads, a drainage system, a large-scale rainwater collection storage system, terracotta brick and statue production, and skilled metal working (in both bronze and precious metals) have been uncovered. According to archaeologists, Rakhigarhi may be the origin of Harappan civilisation, which arose in the Ghaggar basin in Haryana and gradually and slowly moved to the Indus Valley.[23]
During the Vedic era, Haryana was the site of the Kuru Kingdom, one of India's great Mahajanapadas. The south of Haryana is the claimed location of the Vedic Brahmavarta region.[24][better source needed]
Medieval period
Ancient bronze and stone idols of Jain Tirthankara were found in archaeological expeditions in Badli, Bhiwani (Ranila, Charkhi Dadri and Badhra), Dadri, Gurgaon (Gurugram ), Hansi, Hisar, Kasan, Nahad, Narnaul, Pehowa, Rewari, Rohad, Rohtak (Asthal Bohar) and Sonepat in Haryana.[25]

Pushyabhuti dynasty ruled parts of northern India in the 7th century with its capital at Thanesar. Harsha was a prominent king of the dynasty. Tomara dynasty ruled the south Haryana region in the 10th century. Anangpal Tomar was a prominent king among the Tomaras.[26]
After the sack of Bhatner fort during the Timurid conquests of India in 1398, Timur attacked and sacked the cities of Sirsa, Fatehabad, Sunam, Kaithal and Panipat. When he reached the town of Sarsuti (Sirsa), the residents fled and were chased by a detachment of Timur's troops, with thousands of them being killed and looted by the troops. From there he travelled to Fatehabad, whose residents fled and a large number of those remaining in the town were massacred. The Ahirs resisted him at Ahruni but were defeated, with thousands being killed and many being taken prisoners while the town was burnt to ashes. From there he travelled to Tohana, whose Jat inhabitants were stated to be robbers according to Sharaf ad-Din Ali Yazdi. They tried to resist but were defeated and fled. Timur's army pursued and killed 200 Jats, while taking many more as prisoners. He then sent a detachment to chase the fleeing Jats and killed 2,000 of them while their wives and children were enslaved and their property plundered. Timur proceeded to Kaithal whose residents were massacred and plundered, destroying all villages along the way. On the next day, he came to Assandh whose residents were "fire-worshippers" according to Yazdi, and had fled to Delhi. Next, he travelled to and subdued Tughlaqpur fort and Salwan before reaching Panipat whose residents had already fled. He then marched on to Loni fort.[27][28]
![Portrait of Hem Chandra Vikramaditya, who fought and won across North India from the Punjab to Bengal, winning 22 straight battles.[29]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/f/fb/Maharaja_Hemu_Bhargava_-_Victor_of_Twenty_Two_Pitched_Battles%2C_1910s.jpg/220px-Maharaja_Hemu_Bhargava_-_Victor_of_Twenty_Two_Pitched_Battles%2C_1910s.jpg)
Hemu claimed royal status after defeating Akbar's Mughal forces on 7 October 1556 in the Battle of Delhi and assumed the ancient title of Vikramaditya. The area that is now Haryana has been ruled by some of the major empires of India. Panipat is known for three seminal battles in the history of India. In the First Battle of Panipat (1526), Babur defeated the Lodis. In the Second Battle of Panipat (1556), Akbar defeated the local Haryanvi Hindu Emperor of Delhi, who belonged to Rewari. Hem Chandra Vikramaditya had earlier won 22 battles across India from Punjab to Bengal, defeating Mughals and Afghans. Hemu had defeated Akbar's forces twice at Agra and the Battle of Delhi in 1556 to become the last Hindu Emperor of India with a formal coronation at Purana Quila in Delhi on 7 October 1556. In the Third Battle of Panipat (1761), the Afghan king Ahmad Shah Abdali defeated the Marathas.[30]
British Period
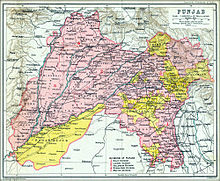
The state was part of the British Punjab province. The Delhi division of Punjab province formed the bulk of Haryana. Among the princely states that were located in the state were Jind, Kalsia, Loharu, Dujana and Pataudi, as well as parts of the Patiala State.
Partition and aftermath
During the Partition of India, the Punjab province was one of two British Indian provinces, alongside Bengal, to be partitioned between India and Pakistan. Haryana, along with other Hindu and Sikh dominated areas of Punjab province, became part of India as East Punjab state. As a result, a significant number of Muslims left for the newly formed country of Pakistan. Similarly, a huge number of Hindu and Sikh refugees poured into the state from West Punjab. Gopi Chand Bhargava, who hailed from Sirsa in present-day Haryana, became the first Chief Minister of East Punjab.
Formation of Haryana
Haryana as a state came into existence on 1 November 1966 the Punjab Reorganisation Act (1966). The Indian government set up the Shah Commission under the chairmanship of Justice JC Shah on 23 April 1966 to divide the existing state of Punjab and determine the boundaries of the new state of Haryana after consideration of the languages spoken by the people. The commission delivered its report on 31 May 1966 whereby the then-districts of Hisar, Mahendragarh, Gurgaon, Rohtak and Karnal were to be a part of the new state of Haryana. Further, the tehsils of Jind and Narwana in the Sangrur district – along with Naraingarh, Ambala and Jagadhri – were to be included.[31]
The commission recommended that the tehsil of Kharar, which includes Chandigarh, the state capital of Punjab, should be a part of Haryana. However Kharar was given to Punjab.[32] The city of Chandigarh was made a union territory, serving as the capital of both Punjab and Haryana.[33]
Bhagwat Dayal Sharma became the first Chief Minister of Haryana.[34]
Demographics
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
|---|---|---|
| 1901 | 4,623,064 | — |
| 1911 | 4,174,677 | −1.02% |
| 1921 | 4,255,892 | +0.19% |
| 1931 | 4,559,917 | +0.69% |
| 1941 | 5,272,829 | +1.46% |
| 1951 | 5,673,597 | +0.74% |
| 1961 | 7,590,524 | +2.95% |
| 1971 | 10,036,431 | +2.83% |
| 1981 | 12,922,119 | +2.56% |
| 1991 | 16,463,648 | +2.45% |
| 2001 | 21,144,564 | +2.53% |
| 2011 | 25,351,462 | +1.83% |
| source:[35] | ||
Religion
Religion in Haryana (2011)[36]
According to the 2011 census, of total 25,351,462 population of Haryana, Hindus (87.46%) constitute the majority of the state's population with Muslims (7.03%) (mainly Meos) and Sikhs (4.91%) being the largest minorities.[36]
Muslims are mainly found in the Nuh. Haryana has the second largest Sikh population in India after Punjab, and they mostly live in the districts adjoining Punjab, such as Sirsa, Jind, Fatehabad, Kaithal, Kurukshetra, Ambala and Panchkula.[37][38]
Languages
The official language of Haryana is Hindi.[40] Several regional languages or dialects, often subsumed under Hindi, are spoken in the state. Predominant among them is Haryanvi (also known as Bangru), whose territory encompasses the central and eastern portions of Haryana. Hindustani is spoken in the northeast, Bagri in the west, and Ahirwati, Mewati and Braj Bhasha in the south.[8]
Punjabi is the most spoken language after Hindi and Haryanvi,[40] and it was recognised as a second official language of Haryana for government and administrative purposes in 2010.[3] There are also many speakers of Multani and Urdu in the state. After the state's formation, Telugu was made the state's "second language" – to be taught in schools – but it was not the "second official language" for official communication. Due to a lack of students, the language ultimately stopped being taught.[41] Tamil was made the second language in 1969 by Bansi Lal to show the state's differences with Punjab although there were no Tamil speakers in Haryana at the time.[42] In 2010, due to the lack of Tamil speakers, the language was removed from its status.[42]
There are also some speakers of several major regional languages of neighbouring states or other parts of the subcontinent, like Bengali, Bhojpuri, Marwari, Mewari, and Nepali,[43] as well as smaller communities of speakers of languages that are dispersed across larger regions, like Bauria, Bazigar, Gujari, Gade Lohar, Oadki, and Sansi.[44]
Culture
Music
Haryana has its own unique traditional folk music, folk dances, saang (folk theatre),[45] cinema,[46] belief system such as Jathera (ancestral worship),[47][48] and arts such as Phulkari and Shisha embroidery.[48]
Folk dances
Folk music and dances of Haryana are based on satisfying cultural needs of primarily agrarian and martial natures of Haryanavi tribes.[49]
Haryanvi musical folk theatre main types are Saang, Rasa lila and Ragini. The Saang and Ragini form of theatre was popularised by Lakhmi Chand.[49]
Haryanvi folk dances and music have fast energetic movements. Three popular categories of dance are: festive-seasonal, devotional, and ceremonial-recreational. The festive-seasonal dances and songs are Gogaji/Gugga, Holi, Phaag, Sawan, Teej. The devotional dances and songs are Chaupaiya, Holi, Manjira, Ras Leela, Raginis). The ceremonial-recreational dances and songs are of following types: legendary bravery (Kissa and Ragini of male warriors and female Satis), love and romance (Been and its variant Nāginī dance, and Ragini), ceremonial (Dhamal Dance, Ghoomar, Jhoomar (male), Khoria, Loor, and Ragini).[47]
Folk music and songs
Haryanvi folk music is based on day to day themes and injecting earthly humour enlivens the feel of the songs.[47] Haryanvi music takes two main forms: "Classical folk music" and "Desi Folk music" (Country Music of Haryana),[50] and sung in the form of ballads and love, valor and bravery, harvest, happiness and pangs of parting of lovers.[49][50][51]
Classical Haryanvi folk music
Classical Haryanvi folk music is based on Indian classical music.[50] Hindustani classical ragas, learnt in gharana parampara of guru–shishya tradition, are used to sing songs of heroic bravery (such as Alha-Khand (1163–1202 CE) about the bravery of Alha and Udal, Jaimal and Patta of Maharana Udai Singh II), Brahmas worship and festive seasonal songs (such as Teej, Holi and Phaag songs of Phalgun month near Holi).[50][51] Bravery songs are sung in high pitch.[49]
Desi Haryanvi folk music
Desi Haryanvi folk music, is a form of Haryanvi music, based on Raag Bhairvi, Raag Bhairav, Raag Kafi, Raag Jaijaivanti, Raag Jhinjhoti and Raag Pahadi and used for celebrating community bonhomie to sing seasonal songs, ballads, ceremonial songs (wedding, etc.) and related religious legendary tales such as Puran Bhagat.[50][51] Relationship and songs celebrating love and life are sung in medium pitch. Ceremonial and religious songs are sung in low pitch.[49] Young girls and women usually sing entertaining and fast seasonal, love, relationship and friendship related songs such as Phagan (song for eponymous season/month), Katak (songs for the eponymous season/month), Samman (songs for the eponymous season/month), bande-bandi (male-female duet songs), sathne (songs of sharing heartfelt feelings among female friends).[49] Older women usually sing devotional Mangal Geet (auspicious songs) and ceremonial songs such as Bhajan, Bhat (wedding gift to the mother of bride or groom by her brother), Sagai, Ban (Hindu wedding ritual where pre-wedding festivities starts), Kuan-Poojan (a custom that is performed to welcome the birth of a child by worshiping the well or source of drinking water), Sanjhi and Holi festival.[49]
Socially normative-cohesive impact
Music and dance for Haryanvi people is a great way of demolishing societal differences as folk singers are highly esteemed and they are sought after and invited for the events, ceremonies and special occasions regardless of their caste or status. These inter-caste songs are fluid in nature, and never personalised for any specific caste, and they are sung collectively by women from different strata, castes, dialects. These songs do transform fluidly in dialect, style, words, etc. This adoptive style can be seen from the adoption of tunes of Bollywood movie songs into Haryanvi songs. Despite this continuous fluid transforming nature, Haryanvi songs have a distinct style of their own as explained above.[49]
With the coming up of a strongly socio-economic metropolitan culture in the emergence of urban Gurgaon (Gurugram) Haryana is also witnessing community participation in public arts and city beautification. Several landmarks across Gurgaon are decorated with public murals and graffiti with cultural cohesive ideologies and stand the testimony of a lived sentiment in Haryana folk.[52]
Cuisine
As per a survey, 13% of males and 7.8% of females of Haryana are non-vegetarian.[53] The regional cuisine features the staples of roti, saag, vegetarian sabzi and milk products such as ghee, milk, lassi and kheer.[54]
Society
Haryanvi people have a concept of inclusive society involving the "36 Jātis" or communities. Castes such as Lohar, Jat, Rajput, Gurjar, Saini, Pasi, Ahirs, Ror, Mev, Charan, Bishnoi, Harijan, Aggarwal, Brahmin, Khatri and Tyagi are some of the notable of these 36 Jātis.[55][56]
Geography

Haryana is a landlocked state in northern India. It is between 27°39' to 30°35' N latitude and between 74°28' and 77°36' E longitude.[57] The total geographical area of the state is 4.42 m ha, which is 1.4% of the geographical area of the country.[58] The altitude of Haryana varies between 700 and 3600 ft (200 metres to 1200 metres) above sea level.[59] Haryana has only 4% (compared with national 21.85%) area under forests.[12] Karoh Peak, a 1,467-metre (4,813 ft) tall mountain peak in the Sivalik Hills range of the greater Himalayas range located near Morni Hills area of Panchkula district, is highest point in Haryana.[60][61][62][63] Most of the state sits atop the fertile Punjab Plain, a subsection of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. Haryana[64] has 4 states and 2 union territories on its border – Punjab, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Himachal Pradesh, Delhi, and Chandigarh.
Plains and mountains
Haryana has four main geographical features.[65]
- The Yamuna-Ghaggar plain forming the largest part of the state is also called Delhi doab consisting of Sutlej-Ghaggar doab (between Sutlej in north in Punjab and Ghaggar river flowing through northern Haryana), Ghaggar-Hakra doab (between Ghaggar river and Hakra or Drishadvati river which is the paleochannel of the holy Saraswati River) and Hakra-Yamuna doab (between Hakra river and Yamuna).
- The Lower Shivalik Hills to the northeast in foothills of Himalaya
- The Bagar tract semi-desert dry sandy plain to the south-west. See also: Bangar and Khadir.
- The Aravali Range's northernmost low rise isolated non-continuous outcrops in the south
Hydrography

The Yamuna, tributary of Ganges, flows along the state's eastern boundary.[66]
Northern Haryana has several north-east to west flowing rivers originating from the Sivalik Hills of Himalayas, such as Ghaggar-Hakra (palaeochannel of vedic Sarasvati river),[67] Chautang (paleochannel of vedic Drishadvati river, tributary of Ghagghar),[68][69] Tangri river (tributary of Ghagghar),[68][69] Kaushalya river (tributary of Ghagghar),[70] Markanda River (tributary of Ghagghar),[68][69] Sarsuti,[68][69] Dangri,[68][69] Somb river.[71] Haryana's main seasonal river, the Ghaggar-Hakra, known as Ghaggar before the Ottu barrage and as the Hakra downstream of the barrage,[67] rises in the outer Himalayas, between the Yamuna and the Satluj and enters the state near Pinjore in the Panchkula district, passes through Ambala and Sirsa, it reaches Bikaner in Rajasthan and runs for 460 km (290 mi) before disappearing into the deserts of Rajasthan.[72] The seasonal Markanda River, known as the Aruna in ancient times, originates from the lower Shivalik Hills and enters Haryana west of Ambala, and swells into a raging torrent during monsoon is notorious for its devastating power, carries its surplus water on to the Sanisa Lake where the Markanda joins the Sarasuti and later the Ghaggar.[72]
Southern Haryana has several south-west to east flowing seasonal rivulets originating from the Aravalli Range in and around the hills in Mewat region, including Sahibi River[73][74][75][76] (called Najafgarh drain in Delhi),[77][78][79][80][81] Dohan river (tributary of Sahibi, originates at Mandoli village near Neem Ka Thana in Jhunjhunu district of Rajasthan and then disappears in Mahendragarh district),[74][76] Krishnavati river (former tributary of Sahibi river, originates near Dariba and disappears in Mahendragarh district much before reaching Sahibi river)[74][76] and Indori river (longest tributary of Sahibi River, originates in Sikar district of Rajasthan and flows to Rewari district of Haryana), these once were tributaries of the Drishadwati/Saraswati river.[82][83][84]

Major canals are Western Yamuna Canal,[85][86][87] Sutlej Yamuna link canal (from Sutlej river tributary of Indus),[86][87] and Indira Gandhi Canal.[88]
Major dams are Kaushalya Dam in Panchkula district,[89] Hathnikund Barrage[85][90] and Tajewala Barrage on Yamuna in Yamunanagar district,[85][90][91] Pathrala barrage on Somb river in Yamunanagar district,[85][91] ancient Anagpur Dam near Surajkund in Faridabad district,[92][93] and Ottu barrage on Ghaggar-Hakra River in Sirsa district.[94][95][96]
Major lakes are Dighal Wetland, Basai Wetland, Badkhal Lake in Faridabad,[97][98] holy Brahma Sarovar[99][100] and Sannihit Sarovar in Kurukshetra,[101] Blue Bird Lake in Hisar,[102][103] Damdama Lake at Sohna in Gurgram district,[104][105] Hathni Kund in Yamunanagar district,[85][90] Karna Lake at Karnal,[106] ancient Surajkund in Faridabad,[92][107][108] and Tilyar Lake in Rohtak.[109][110][111]
The Haryana State Waterbody Management Board is responsible for rejuvenation of 14,000 Johads of Haryana and up to 60 lakes in National Capital Region falling within the Haryana state.[112][113]
Only hot spring of Haryana is the Sohna Sulphur Hot Spring at Sohna in Gurgaon district.[114][115] Tosham Hill range has several sacred sulphur pond of religious significance that are revered for the healing impact of sulphur, such as Pandu Teerth Kund, Surya Kund, Kukkar Kund, Gyarasia Kund or Vyas Kund.[116]
Seasonal waterfalls include Tikkar Taal twin lakes at Morni hiills, Dhosi Hill in Mahendragarh district and Pali village on outskirts of Faridabad.
Climate
Haryana is hot in summer at around 45 °C (113 °F) and mild in winter. The hottest months are May and June and the coldest December and January.[82] The climate is arid to semi-arid with average rainfall of 354.5 mm. Around 29% of rainfall is received during the months from July to September as a result of the Monsoon, and the remaining rainfall is received during the period from December to February as a result of the Western Disturbance.[58]
| Climate data for Gurgaon (1981–2010, extremes 1965–2000) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 28.0 (82.4) |
33.5 (92.3) |
39.5 (103.1) |
44.8 (112.6) |
49.0 (120.2) |
47.5 (117.5) |
45.0 (113.0) |
41.0 (105.8) |
41.2 (106.2) |
39.3 (102.7) |
38.4 (101.1) |
32.5 (90.5) |
49.0 (120.2) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 20.7 (69.3) |
23.7 (74.7) |
29.6 (85.3) |
36.6 (97.9) |
40.2 (104.4) |
39.8 (103.6) |
35.5 (95.9) |
34.0 (93.2) |
34.1 (93.4) |
32.8 (91.0) |
28.3 (82.9) |
23.1 (73.6) |
31.5 (88.7) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 6.4 (43.5) |
8.8 (47.8) |
13.5 (56.3) |
19.1 (66.4) |
24.1 (75.4) |
26.5 (79.7) |
26.4 (79.5) |
25.6 (78.1) |
23.8 (74.8) |
17.3 (63.1) |
11.3 (52.3) |
7.0 (44.6) |
17.5 (63.5) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 0.0 (32.0) |
0.7 (33.3) |
3.7 (38.7) |
9.2 (48.6) |
14.8 (58.6) |
12.0 (53.6) |
21.0 (69.8) |
15.5 (59.9) |
13.9 (57.0) |
9.3 (48.7) |
2.6 (36.7) |
−0.4 (31.3) |
−0.4 (31.3) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 15.0 (0.59) |
21.4 (0.84) |
12.3 (0.48) |
18.2 (0.72) |
34.3 (1.35) |
57.3 (2.26) |
171.4 (6.75) |
190.7 (7.51) |
93.8 (3.69) |
12.0 (0.47) |
10.7 (0.42) |
9.9 (0.39) |
657.0 (25.87) |
| Average rainy days | 1.2 | 1.6 | 1.2 | 1.1 | 2.2 | 3.6 | 7.6 | 8.3 | 4.6 | 1.0 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 34.2 |
| Average relative humidity (%) (at 17:30 IST) | 54 | 45 | 37 | 28 | 31 | 40 | 63 | 69 | 59 | 45 | 47 | 55 | 48 |
| Source: India Meteorological Department[117][118] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Rohtak (1981–2010, extremes 1967–2012) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 30.4 (86.7) |
33.6 (92.5) |
40.0 (104.0) |
45.0 (113.0) |
46.8 (116.2) |
47.2 (117.0) |
44.9 (112.8) |
41.3 (106.3) |
40.5 (104.9) |
39.4 (102.9) |
37.0 (98.6) |
30.3 (86.5) |
47.2 (117.0) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 20.5 (68.9) |
24.0 (75.2) |
29.7 (85.5) |
36.9 (98.4) |
39.9 (103.8) |
39.6 (103.3) |
36.2 (97.2) |
34.4 (93.9) |
34.6 (94.3) |
33.6 (92.5) |
29.0 (84.2) |
23.6 (74.5) |
31.8 (89.2) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 6.9 (44.4) |
9.7 (49.5) |
14.4 (57.9) |
20.0 (68.0) |
24.9 (76.8) |
26.6 (79.9) |
26.9 (80.4) |
26.0 (78.8) |
24.1 (75.4) |
18.2 (64.8) |
11.9 (53.4) |
7.5 (45.5) |
18.1 (64.6) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −0.5 (31.1) |
0.2 (32.4) |
2.0 (35.6) |
10.4 (50.7) |
10.5 (50.9) |
19.0 (66.2) |
19.4 (66.9) |
21.1 (70.0) |
15.0 (59.0) |
8.3 (46.9) |
2.9 (37.2) |
0.0 (32.0) |
−0.5 (31.1) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 14.0 (0.55) |
16.6 (0.65) |
10.7 (0.42) |
14.2 (0.56) |
34.8 (1.37) |
66.5 (2.62) |
150.8 (5.94) |
192.4 (7.57) |
76.4 (3.01) |
12.8 (0.50) |
2.2 (0.09) |
5.5 (0.22) |
597.0 (23.50) |
| Average rainy days | 1.2 | 1.6 | 1.3 | 1.0 | 2.1 | 3.4 | 6.9 | 6.5 | 3.6 | 0.7 | 0.3 | 0.6 | 29.2 |
| Average relative humidity (%) (at 17:30 IST) | 60 | 50 | 43 | 27 | 29 | 42 | 64 | 70 | 59 | 47 | 51 | 57 | 50 |
| Source: India Meteorological Department[117] | |||||||||||||
Flora and fauna
| Formation day | 1 November (Day of separation from Punjab) |
| State mammal | Black buck[119] |
| State bird | Black francolin |
| State tree | Peepal[119] |
| State flower | Lotus[119] |
Forests
Forest cover in the state in 2013 was 3.59% (1586 km2) and the Tree Cover in the state was 2.90% (1282 km2), giving a total forest and tree cover of 6.49%.[120] In 2016–17, 18,412 hectares were brought under tree cover by planting 14.1 million seedlings.[12] Thorny, dry, deciduous forest and thorny shrubs can be found all over the state. During the monsoon, a carpet of grass covers the hills. Mulberry, eucalyptus, pine, kikar, shisham and babul are some of the trees found here. The species of fauna found in the state of Haryana include black buck, nilgai, panther, fox, mongoose, jackal and wild dog. More than 450 species of birds are found here.[121][122][123]
Wildlife

Haryana has two national parks, eight wildlife sanctuaries, two wildlife conservation areas, four animal and bird breeding centers, one deer park and three zoos, all of which are managed by the Haryana Forest Department of the Government of Haryana.[124][125] Sultanpur National Park is a notable Park located in Gurugram District
Environmental and ecological issues
Haryana Environment Protection Council is the advisory committee and Department of Environment, Haryana is the department responsible for the administration of environment. Areas of Haryana surrounding Delhi NCR are the most polluted. During smog of November 2017, Air quality index of Gurgaon and Faridabad showed that the density of Fine particulates (2.5 PM diameter) was an average of 400 PM and monthly average of Haryana was 60 pm. Other sources of pollution are exhaust gases from old vehicles, stone crushers and Brick Kiln. Haryana has 7.5 million old vehicles, of which 40% are old more polluting vehicles, besides 500,000 new vehicles are added every year. Other majorly polluted cities are Bhiwani, Bahadurgarh, Dharuhera, Hisar and Yamunanagar.[126]
Administration
Divisions

The state is divided into 6 revenue divisions, 5 Police Ranges and 3 Police Commissionerates (c. January 2017).[127][128][129][130] Six revenue divisions are: Ambala, Rohtak, Gurgaon, Hisar, Karnal and Faridabad.[127] Haryana has 11 municipal corporations (Gurgaon, Faridabad, Ambala, Panchkula, Yamunanagar, Rohtak, Hisar, Panipat, Karnal, Sonepat, and Manesar[131]), 18 municipal councils and 52 municipalities.[132]
Within these there are 22 districts, 72 sub-divisions, 93 tehsils, 50 sub-tehsils, 140 blocks, 154 cities and towns, 6,848 villages, 6,222 villages panchayats and numerous smaller dhanis.[14]
Districts
| Divisions | Districts |
|---|---|
| Ambala | Ambala, Kurukshetra, Panchkula, Yamuna Nagar |
| Faridabad | Faridabad, Palwal, Nuh |
| Gurgaon | Gurgaon, Mahendragarh, Rewari, |
| Hisar | Fatehabad, Jind, Hisar, Sirsa, |
| Rohtak | Jhajjar, Charkhi Dadri, Rohtak, Sonipat, Bhiwani[65] |
| Karnal | Karnal, Panipat, Kaithal |
Law and order
Haryana Police force is the law enforcement agency of Haryana. Five Police Ranges are Ambala, Hissar, Karnal, Rewari and Rohtak.[133] Three Police Commissionerates are Faridabad, Gurgaon and Panchkula.[127] Cybercrime investigation cell is based in Gurgaon's Sector 51.[134]
The highest judicial authority in the state is the Punjab and Haryana High Court, with next higher right of appeal to Supreme Court of India. Haryana uses an e-filing facility.[135]
Governance and e-governance
The Common Service Centres (CSCs) have been upgraded in all districts to offer hundreds of e-services to citizens, including applications of new water and sanitation connections, electricity bill collection, ration card member registration, result of HBSE, admit cards for board examinations, online admission forms for government colleges, long route booking of buses, admission forms for Kurukshetra University and HUDA plots status inquiry.[136] Haryana has become the first state to implement Aadhaar-enabled birth registration in all the districts.[136] Thousands of all traditional offline state and central government services are also available 24/7 online through single unified UMANG app and portal as part of Digital India initiative.[137][138]
Economy

Haryana's 14th placed 12.96% 2012-17 CAGR[15] estimated 2017-18 GSDP of US$95 billion[12] is split in to 52% services, 30% industries and 18% agriculture.[12]
Services sector is split across 45% in real estate and financial and professional services, 26% trade and hospitality, 15% state and central govt employees, and 14% transport and logistics & warehousing.[12] In IT services, Gurugram ranks number 1 in India in growth rate and existing technology infrastructure, and number 2 in startup ecosystem, innovation and livability (Nov 2016).[139]
Industries sector is split across 69% manufacturing, 28% construction, 2% utilities and 1% mining.[12] In industrial manufacturing, Haryana produces India's 67% of passenger cars, 60% of motorcycles, 50% of tractors and 50% of the refrigerators.[12]
Services and industrial sectors are boosted by 7 operational SEZs and additional 23 formally approved SEZs (20 already notified and 3 in-principal approval) that are mostly spread along the Delhi–Mumbai Industrial Corridor, Amritsar Delhi Kolkata Industrial Corridor and Western Peripheral Expressway.[12]
Agriculture sector is split across 93% crops and livestock, 4% commercial forestry and logging, and 2% fisheries.[12] Agriculture sector of Haryana, with only less than 1.4% area of India, contributes 15% food grains to the central food security public distribution system,[12] and 7% of total national agricultural exports including 60% of total national Basmati rice export.[12]
Agriculture
Crops

Haryana is traditionally an agrarian society of zamindars (owner-cultivator farmers). About 70% of Haryana's residents are engaged in agriculture.[140] The Green Revolution in Haryana of the 1960s[141] combined with completion of Bhakra Dam in 1963[142] and Western Yamuna Command Network canal system in 1970s resulted in the significantly increased food grain production.[141] As a result, Haryana is self sufficient in food production and the second largest contributor to India's central pool of food grains [143] In 2015–2016, Haryana produced the following principal crops: 13,352,000 tonne wheat, 4,145,000 tonne rice, 7,169,000 tonne sugarcane, 993,000 tonne cotton and 855,000 tonne oilseeds (mustard seed, sunflower, etc.).
Fruits, vegetables and spices
Vegetable production was: potato 853,806 tonnes, onion 705,795 tonnes, tomato 675,384 tonnes, cauliflower 578,953 tonnes, leafy vegetables 370,646 tonnes, brinjal 331,169 tonnes, guard 307,793 tonnes, peas 111,081 tonnes and others 269,993 tonnes.[12]
Fruits production was: citrus 301,764 tonnes, guava 152,184 tonnes, mango 89,965 tonnes, chikoo 16,022 tonnes, aonla 12,056 tonnes and other fruits 25,848 tonnes.[12]
Spices production was: garlic 40,497 tonnes, fenugreek 9,348 tonnes, ginger 4,304 tonnes and others 840 tonnes.[12]
Flowers and medicinal plants
Cut flowers production was: marigold 61,830 tonnes, gladiolus 2,448,620 million, rose 1,861,160 million and other 691,300 million.[12]
Medicinal plants production was: aloe vera 1403 tonnes and stevia 13 tonnes.[12]
Livestock
Haryana is well known for its high-yield Murrah buffalo.[144][145][146][147] Other breeds of cattle native to Haryana are Haryanvi, Mewati, Sahiwal and Nili-Ravi.[148]
Research
To support its agrarian economy, both central government (Central Institute for Research on Buffaloes, Central Sheep Breeding Farm, National Research Centre on Equines, Central Institute of Fisheries, National Dairy Research Institute, Regional Centre for Biotechnology, Indian Institute of Wheat and Barley Research and National Bureau of Animal Genetic Resources) and state government (CCS HAU, LUVAS, Government Livestock Farm, Regional Fodder Station and Northern Region Farm Machinery Training and Testing Institute) have opened several institutes for research and education.[149][150][151]
Industrial sector
Manufacturing


- Faridabad is one of the biggest industrial cities of Haryana as well as North India.[152] The city is home to large-scale MNC companies like India Yamaha Motor Pvt. Ltd., Havells India Limited,[153] JCB India Limited, Escorts Group, Indian Oil (R&D),[154] and Larsen & Toubro (L&T).[155] Eyewear e-tailer Lenskart and healthcare startup Lybrate have their headquarters in Faridabad.[156][157]
- Hissar, a NCR Counter Magnet city known as steel and cotton spinning hub as well as upcoming integrated industrial aerocity and aero MRO hub at Hisar Airport,[158][159][160] is a fast developing city and the hometown of Navin Jindal and Subhash Chandra of Zee TV fame. Savitri Jindal, Navin Jindal's mother, has been listed by Forbes as the third richest woman in the world.[161]
- Panipat has heavy industry, including a refinery operated by the Indian Oil Corporation, a urea manufacturing plant operated by National Fertilizers Limited and a National Thermal Power Corporation power plant. It is known for its woven modhas or round stools.[162]
- Sonipat: IMT Kundli, Nathupur, Rai and Barhi are industrial areas with several Small and medium-sized enterprises, including come large ones such as Atlas cycles, E.C.E., Birla factory, OSRAM[163][164][165]
- Gurgaon: IMT Minesar, Dundahera and Sohna are industrial and logistics hubs,[166][167][168] that also has National Security Guards, Indian Institute of Corporate Affairs, National Brain Research Centre and National Bomb Data Centre.[169]
Utilities
Haryana State has always given high priority to the expansion of electricity infrastructure, as it is one of the most important inputs for the development of the state. Haryana was the first state in the country to achieve 100% rural electrification in 1970 as well as the first in the country to link all villages with all-weather roads and provide safe drinking water facilities throughout the state.[170][better source needed]
Power in the state are:
- Renewable and non-polluting sources
- Hydroelectricity
- Bhakra-Nangal Dam Hydroelectric Power Plant
- WYC Hydro Electric Station, 62.4 MW, Yamunanagar[171]
- Solar power stations
- Faridabad Solar Power Plant: being set up by HPGCL Faridabad (c.2016).[172]
- Hydroelectricity
- Nuclear power stations
- Coal-fired thermal power stations
- Deenbandhu Chhotu Ram Thermal Power Station, 600MW, Yamunanagar[171]
- Indira Gandhi Super Thermal Power Project, 1500MW, Jhajjar[171]
- Jhajjar Power Station, 1500MW[171]
- Panipat Thermal Power Station I, 440MW[171]
- Panipat Thermal Power Station II, 920MW[171]
- Rajiv Gandhi Thermal Power Station, 1200MW, Hisar[171]
Services sector
Transport

Aviation
Roads and Highways
Haryana has a total road length of 26,062 kilometres (16,194 mi), including 2,482 kilometres (1,542 mi) 29 national highways, 1,801 kilometres (1,119 mi) state highways,[175] 1,395 kilometres (867 mi) Major District Roads (MDR) and 20,344 kilometres (12,641 mi) Other District Roads (ODR) (c. December 2017).[176] A fleet of 3,864 Haryana Roadways buses covers a distance of 1.15 million km per day, and it was the first state in the country to introduce luxury video coaches.[177]
Ancient Delhi Multan Road and Grand Trunk Road, South Asia's oldest and longest major roads, pass through Haryana. GT Road passes through the districts of Sonipat, Panipat, Karnal, Kurukshetra and Ambala in north Haryana where it enters Delhi and subsequently the industrial town of Faridabad on its way. The 135.6 kilometres (84.3 mi) Kundli-Manesar-Palwal Expressway (KMP) will provide a high-speed link to northern Haryana with its southern districts such as Sonipat, Gurgaon, and Faridabad.[178]
The Delhi-Agra Expressway (NH-2) that passes through Faridabad is being widened to six lanes from current four lanes.[179] It will further boost Faridabad's connectivity with Delhi.
Railway
Rail network in Haryana is covered by five rail divisions under three rail zones. Diamond Quadrilateral High-speed rail network,[180] Eastern Dedicated Freight Corridor (72 km)[181] and Western Dedicated Freight Corridor (177 km)[182] pass through Haryana.
Bikaner railway division of North Western Railway zone manages rail network in western and southern Haryana covering Bhatinda-Dabwali-Hanumangarh line, Rewari-Bhiwani-Hisar-Bathinda line, Hisar-Sadulpur line and Rewari-Loharu-Sadulpur line.[183][184] Jaipur railway division of North Western Railway zone manages the rail network in south-west Haryana covering Rewari-Reengas-Jaipur line, Delhi-Alwar-Jaipur line and Loharu-Sikar line.[185]
Delhi railway division of Northern Railway zone manages the rail network in north and east and central Haryana covering Delhi-Panipat-Ambala line, Delhi-Rohtak-Tohana line, Rewari–Rohtak line, Jind-Sonepat line and Delhi-Rewari line.[186][187][188][189][190] Agra railway division of North Central Railway zone manages another very small part of the network in south-east Haryana covering Palwal-Mathura line only.[191][192]
Ambala railway division of Northern Railway zone manages a small part of the rail network in north-east Haryana covering Ambala-Yamunanagar line, Ambala-Kurukshetra line and UNESCO World Heritage Kalka–Shimla Railway.[193]
Metro
Delhi Metro connects the national capital Delhi with NCR cities of Faridabad, Gurgaon and Bahadurgarh. Faridabad has the longest metro network in the NCR Region consisting of 11 stations and track length being 17 km.[194]
Sky Way

The Haryana and Delhi governments have constructed the 4.5-kilometre (2.8 mi) international standard Delhi Faridabad Skyway, the first of its kind in North India, to connect Delhi and Faridabad.[195]
Communication and media
Haryana has a statewide network of telecommunication facilities. Haryana Government has its own statewide area network by which all government offices of 22 districts and 126 blocks across the state are connected with each other thus making it the first SWAN of the country.[196][197][198] Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited and most of the leading private sector players (such as Reliance Infocom, Tata Teleservices, Bharti Telecom, Idea Vodafone Essar, Aircel, Uninor and Videocon) have operations in the state. Two biggest cities of Haryana, Faridabad and Gurgaon which are part of National Capital Region come under the local Delhi Mobile Telecommunication System. The rest of the cities of Haryana comes under Haryana Telecommunication System.
Electronic media channels include, MTV, 9XM, Star Group, SET Max, News Time, NDTV 24x7 and Zee Group. The radio stations include All India Radio and other FM stations.
Panipat, Hisar, Ambala and Rohtak are the cities in which the leading newspapers of Haryana are printed and circulated throughout Haryana, in which Dainik Bhaskar, Dainik Jagran, Punjab Kesari, The Tribune, Aaj Samaj, Hari Bhoomi[199] and Amar Ujala are prominent.
Healthcare

The total fertility rate of Haryana is 2.3. The infant mortality rate is 41 (SRS 2013) and maternal mortality ratio is 146 (SRS 2010–2012).[200] The state of Haryana has various Medical Colleges including Pandit Bhagwat Dayal Sharma Post Graduate Institute of Medical Sciences Rohtak, Bhagat Phool Singh Medical College in District Sonipat, ESIC Medical College, Faridabad along with notable private medical institutes like Medanta, Max Hospital, Fortis Healthcare
Education
Literacy
Literacy rate in Haryana has seen an upward trend and is 76.64 per cent as per 2011 population census. Male literacy stands at 85.38 per cent, while female literacy is at 66.67 per cent. In 2001, the literacy rate in Haryana stood at 67.91 per cent of which male and female were 78.49 per cent and 55.73 per cent literate respectively.[201] As of 2013[update], Gurgaon city had the highest literacy rate in Haryana at 86.30% followed by Panchkula at 81.9 per cent and Ambala at 81.7 per cent.[202] In terms of districts, as of 2012[update] Rewari had the highest literacy rate in Haryana at 74%, higher than the national average of 59.5%: male literacy was 79%, and female 67%.[203]
Schools
Haryana Board of School Education, established in September 1969 and shifted to Bhiwani in 1981, conducts public examinations at middle, matriculation, and senior secondary levels twice a year. Over 700,000 candidates attend annual examinations in February and March; 150,000 attend supplementary examinations each November. The Board also conducts examinations for Haryana Open School at senior and senior secondary levels twice a year.[204] The Haryana government provides free education to women up to the bachelor's degree level.
In 2015–2016, there were nearly 20,000 schools, including 10,100 state government schools (36 Aarohi Schools, 11 Kasturba Gandhi Balika Vidyalayas, 21 Model Sanskriti Schools, 8,744 government primary school, 3386 government middle school, 1,284 government high school and 1,967 government senior secondary schools),[205] 7,635 private schools (200 aided,[206] 6,612 recognised unaided,[207] and 821 unrecognised unaided private schools[208]) and several hundred other central government and private schools such as Kendriya Vidyalaya, Indian Army Public Schools, Jawahar Navodaya Vidyalaya and DAV schools affiliated to central government's CBSE and ICSE school boards.
Universities and higher education

Haryana has 48 universities and 1,038 colleges,[209] including 115 government colleges, 88 government-aided colleges and 96 self-finance colleges.[210] Hisar has three universities: Chaudhary Charan Singh Haryana Agricultural University – Asia's largest agricultural university,[211] Guru Jambheshwar University of Science and Technology, Lala Lajpat Rai University of Veterinary & Animal Sciences); several national agricultural and veterinary research centres (National Research Centre on Equines),[212] Central Sheep Breeding Farm,[213] National Institute on Pig Breeding and Research,[214] Northern Region Farm Machinery Training and Testing Institute[215] and Central Institute for Research on Buffaloes (CIRB);[216] and more than 20 colleges including Maharaja Agrasen Medical College, Agroha.[217]
Demographically, Haryana has 471,000 women and 457,000 men pursuing post-secondary school higher education. There are more 18,616 female teachers and 17,061 male teachers in higher education.[209]
Union Minister Ravi Shankar Prasad announced on 27 February 2016 that National Institute of Electronics and Information Technology (NIELIT) would be set up in Kurukshetra to provide computer training to youth and a Software Technology Park of India (STPI) would be set up in Panchkula's existing HSIIDC IT Park in Sector 23.[218] Hindi and English are compulsory languages in schools whereas Punjabi, Sanskrit and Urdu are chosen as optional languages.[219]
Sports

In the 2010 Commonwealth Games at Delhi, 22 out of 38 gold medals that India won came from Haryana.[220] During the 33rd National Games held in Assam in 2007, Haryana stood first in the nation[221] with a medal tally of 80, including 30 gold, 22 silver and 28 bronze medals.
The 1983 World Cup winning captain Kapil Dev made his domestic-cricket debut playing for Haryana. Nahar Singh Stadium was built in Faridabad in the year 1981 for international cricket. This ground has the capacity to hold around 25,000 people as spectators.[222] Tejli Sports Complex is an ultra-modern sports complex in Yamuna Nagar. Tau Devi Lal Stadium in Gurgaon is a multi-sport complex.[223]
Chief Minister of Haryana Manohar Lal Khattar announced the "Haryana Sports and Physical Fitness Policy", a policy to support 26 Olympic sports, on 12 January 2015 with the words "We will develop Haryana as the sports hub of the country."[224][225]
Haryana is home to Haryana Gold, one of India's eight professional basketball teams which compete in the country's UBA Pro Basketball League.
At the 2016 Summer Olympics, Sakshi Malik won the bronze medal in the 58 kg category, becoming the first Indian female wrestler to win a medal at the Olympics and the fourth female Olympic medalist from the country.
Notable Badminton Player, Saina Nehwal is from Hisar in Haryana.[226]
Notable Athlete, Neeraj Chopra , who competes in Javelin Throw and won the first track and field gold medal in 2020 Tokyo Olympics for India, was born and raised in Panipat, Haryana. Wrestling is also very prominent in Haryana as 2 medals won in wrestling at 2020 Tokyo Olympics were from Haryana.
Notable Athlete, Ravi Dahiya, who was born in Nahri village of Sonipat District. Won Silver Medal in 2020 Tokyo Olympics for India.
Bajrang Punia-Bronze Medal. Ravi Kumar,[2] is an Indian freestyle wrestler who won a silver medal at the 2020 Tokyo Olympics in the 57 kg category. Dahiya is also a bronze medalist from 2019 World Wrestling Championships and a two-time Asian champion.
See also
- List of Monuments of National Importance in Haryana
- List of State Protected Monuments in Haryana
- List of people from Haryana
- Outline of Haryana
- Politics of Haryana
- Tourism in Haryana
- Haryanvi cinema
- List of earthquakes in Haryana
References
- "Haryana at a Glance". Government of Haryana. Archived from the original on 14 March 2016. Retrieved 1 March 2016.
- "Report of the Commissioner for linguistic minorities: 52nd report (July 2014 to June 2015)" (PDF). Commissioner for Linguistic Minorities, Ministry of Minority Affairs, Government of India. pp. 85–86. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 November 2016. Retrieved 16 February 2016.
- "Haryana grants second language status to Punjabi". Hindustan Times. Indo-Asian News Service. 28 January 2010. Archived from the original on 5 November 2018. Retrieved 2 January 2019.
- "The way tough Haryanvis speak". The Tribune. 28 December 2019. Retrieved 28 March 2020.
- "Social Status of a Haryanvi Rural Woman: A Reflective Study through Folk Songs". iitd.ac.com. Archived from the original on 20 February 2020. Retrieved 28 March 2020.
- "No takers in their own land". Tribune. 7 April 2019. Retrieved 1 May 2022.
- "PressReader.com - Your favorite newspapers and magazines". pressreader.com.
- Sharada, Sadhu Ram, ed. (c. 1979). Hariyāṇā kī upabhāṣāeṃ (in Hindi). Chandigarh: Bhasha Vibhag.
- "Economic Survey of Haryana 2020-21" (PDF). Government of Haryana. 1 February 2022. pp. 2–3. Retrieved 1 February 2022.
- "Sub-national HDI - Area Database". Global Data Lab. Institute for Management Research, Radboud University. Archived from the original on 23 September 2018. Retrieved 24 October 2018.
- "Haryana Population Sex Ratio in Haryana Literacy rate data". Census Commission of India. Archived from the original on 15 August 2017. Retrieved 13 August 2017.
- "Haryana State Budget 2017-18" (PDF). Haryana Finance Dept. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 August 2017. Retrieved 7 October 2017.
- "This is NCR's new foodie magnet; have you been yet?". India Today. 26 March 2017. Archived from the original on 22 April 2017. Retrieved 21 April 2017.
- NIDM, p. 4.
- Industrial Development & Economic Growth in Haryana Archived 6 October 2018 at the Wayback Machine, India Brand Equity Foundation, Nov 2017.
- "Gurugram among top 5 IT hubs in Asia Pacific". Hindustan Times. 28 May 2019. Retrieved 28 May 2019.
- Julka, Harsimran (30 September 2011). "IT firms looking beyond Gurgaon, Noida, Greater Noida to other cities in north India". The Economic Times. ET Bureau. Archived from the original on 5 November 2013. Retrieved 2 October 2013.
- "Unemployment Rate in India". Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy. p. 1. Retrieved 1 April 2021.
- Lal, Muni (1974). Haryana: On High Road to Prosperity. Vikas Publishing House. ISBN 978-0-7069-0290-7.
- Punia, Bijender K. (1994). Tourism Management: Problems and Prospects. APH Publishing. ISBN 978-81-7024-643-5.
- Chopra, Pran Nath (1982). Religions and Communities of India. Vision Books. ISBN 978-0-391-02748-0.
- Subramanian, T. S. (27 March 2014). "Rakhigarhi, the biggest Harappan site". The Hindu.
- Subramanian, T. S. (27 March 2014), "Rakhigarhi, the biggest Harappan site", The Hindu, archived from the original on 27 November 2016, retrieved 24 January 2016
- "The Tribune, Chandigarh, India - Haryana Plus". The Tribune. Archived from the original on 31 October 2016. Retrieved 4 August 2016.
- Atul Kumar Sinha & Abhay Kumar Singh 2007, p. 401.
- "Explained: The legacy of Tomar king Anangpal II and his connection with Delhi". The Indian Express. 22 March 2021. Retrieved 6 May 2021.
- Elliot, Sir Henry Miers; Dowson, John (1871). The History of India, as Told by Its Own Historians. The Muhammadan Period: Ed. from the Posthumous Papers of the Late Sir H. M. Elliot . Trübner and Company. pp. 427–31.
- Phadke, H.A. (1990). Haryana, Ancient and Medieval. Harman Publishing House. p. 123.
- Sarkar 1960, p. 66.
- Arnold P. Kaminsky; Roger D. Long (2011). India Today: An Encyclopedia of Life in the Republic. ABC-CLIO. p. 300. ISBN 978-0-313-37462-3. Archived from the original on 19 June 2016. Retrieved 13 February 2016.
- the punjab reorganisation act, 1966 - Chief Secretary, Haryana (PDF), archived (PDF) from the original on 4 March 2016, retrieved 12 November 2015
- History of Haryana - Haryana Day: A new state is born!, archived from the original on 2 October 2013
- Haryana will get Chandigarh, Punjab can claim Lahore or Shimla, says a peeved Hooda, 25 July 2013, archived from the original on 17 November 2015, retrieved 15 November 2015
- "List of Haryana Chief Ministers from November 1, 1966 till date", The Indian Express, 21 October 2014, archived from the original on 30 October 2015, retrieved 12 November 2015
- "Decadal Variation in Population Since 1901". Retrieved 18 March 2020.
- "Population by religion community - 2011". Census of India, 2011. The Registrar General & Census Commissioner, India. Archived from the original on 25 August 2015.
- "Haryana government announced the formation of rules to register Anand Karaj, the Sikh marriage ceremony". Archived from the original on 15 July 2014. Retrieved 13 July 2014.
- Govt. of India, Census (2001). "Census India 2001" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 November 2011. Retrieved 28 March 2013.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 12 January 2020. Retrieved 11 October 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - "Report of the Commissioner for linguistic minorities: 50th report (July 2012 to June 2013)" (PDF). Commissioner for Linguistic Minorities, Ministry of Minority Affairs, Government of India. p. 11. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 July 2016. Retrieved 4 December 2016.
- Bhatia, Varinder (6 February 2019). "Haryana's South connect: When it made Telugu second language in school". The Indian Express. Retrieved 18 March 2020.
- Bharadwaj, Ajay (7 March 2010). "Punjabi edges out Tamil in Haryana". DNA India.
- Bengali and Bhojpuri are listed as they have more than 50,000 speakers each according to the 2011 census; the rest are included following Ethnologue.
- Eberhard, David M.; Simons, Gary F.; Fennig, Charles D., eds. (2019). "India – Languages". Ethnologue (22nd ed.). SIL International. Archived from the original on 1 April 2019.
- Sachchidananda Encyclopaedic Profile of Indian Tribes Volume 1 - 1996 817141298X p416.
- Bhatia, Sheveta (17 August 2010). "Second Innings". The Indian Express. Retrieved 17 March 2011.
- "Journal of Punjab Studies - Center for Sikh and Punjab Studies - UC Santa Barbara". global.ucsb.edu. Archived from the original on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 4 December 2017.
- A Glossary of the tribes & castes of Punjab by H. A Rose
- Manorma Sharma, 2007, Musical Heritage of India, Page 65-125.
- S. C. Bhatt and Gopal K. Bhargava, 2006, Land and People of Indian States and Union Territories: 21 Arts and Crafts of Haryana.
- S. Gajrani, 2004, History, Religion and Culture of India, Volume 1, Page 96.
- Patra, Pratyush (25 March 2016). "Artists give Gurgaon's walls a makeover". The Times of India. Retrieved 6 November 2019.
- "Most Indians are non-vegetarian, Southern and Northeastern states top the list: Report". Business Today. 22 May 2018. Retrieved 12 August 2020.
- Cuisine of Haryana Archived 4 December 2017 at the Wayback Machine, Haryana Tourism.
- Sāṅgavāna, Guṇapālasiṃha (1989). Harayāṇavī lokagītoṃ kā sāṃskr̥tika adhyayana (in Hindi). Hariyāṇā Sāhitya Akādamī. p. 17.
- "Social study the KhapPanchayats of Haryana: A Survey, International Journal of Research in Social Sciences Vol. 7 Issue 11" (PDF). Open J-Gage as well as in Cabell's Directories of Publishing Opportunities, U.S.A.
- NIDM, p. 2.
- Home, Department of Agriculture (Haryana), archived from the original on 17 November 2015
- Organizations, archived from the original on 14 November 2018, retrieved 19 December 2018
- "Hills of Morni". hillsofmorni.com. 27 September 2014. Archived from the original on 14 March 2016. Retrieved 24 March 2016.
- "Interesting Facts About Haryana". quickgs.com. 7 May 2015. Archived from the original on 12 March 2016. Retrieved 24 March 2016.
- "Karoh Peak". Peakbagger.com. Retrieved 24 March 2016.
- "Gazetteer of India". University of Chicago. Archived from the original on 5 April 2016. Retrieved 24 March 2016.
- "Haryana Gk Questions". Current Affairs. 12 December 2021. Retrieved 8 January 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - NIDM, p. 3.
- "River Saraswati is for real, found in Haryana", Zee Nees, 8 May 2015, archived from the original on 20 November 2015, retrieved 12 November 2015
-
Dale Hoiberg; Indu Ramchandani (2000). Students' Britannica India, Volumes 1-5. Popular Prakashan, 2000. ISBN 978-0-85229-760-5. Archived from the original on 6 December 2017. Retrieved 13 November 2017.
... The Ghaggar River rises in the Shiwalik Range, northwestern Himachal Pradesh State, and flows about 320 km southwest through Haryana State, where it receives the Saraswati River. Beyond the Otu Barrage, the Ghaggar River is known as the Hakra River which loses itself in the Thar Desert. Just southwest of Sirsa it feeds two irrigation canals that extend into Rajasthan. ...
- "Rivers in Ambala, Markanda River Ambala, Tangri River Ambala". ambalaonline.in. Archived from the original on 13 November 2017. Retrieved 4 December 2017.
- Chopra, Sanjeev (25 September 2010). "Overflowing Ghaggar, Tangri inundate some villages along Punjab-Haryana border". The Indian Express. Archived from the original on 28 June 2018. Retrieved 9 April 2017.
- "Kaushalya Dam". 13 December 2012. Archived from the original on 14 November 2017. Retrieved 4 December 2017.
- "HaryanaOnline - Geography of Haryana". Archived from the original on 1 February 2016. Retrieved 4 December 2017.
- Geography- others, District Administration, Kurukshetra, archived from the original on 2 May 2018, retrieved 1 December 2018
- Cultural Contours of India: Dr. Satya Prakash Felicitation Volume, Vijai Shankar Śrivastava, 1981. ISBN 0391023586
- "Sahibi river". Archived from the original on 12 October 2017. Retrieved 4 December 2017.
- Jain, A.K. (4 December 2017). River Pollution. APH Publishing. ISBN 9788131304631. Retrieved 4 December 2017 – via Google Books.
- Minerals and Metals in Ancient India: Archaeological evidence, Arun Kumar Biswas, Sulekha Biswas, University of Michigan. 1996. ISBN 812460049X.
- "Latest News, Breaking News Live, Current Headlines, India News Online - The Indian Express". The Indian Express. Retrieved 4 December 2017.[permanent dead link]
- Environment Minister raises a stink over Najafgarh jheel[permanent dead link], 22 February 2005, The Indian Express
- Najafgarh basin Delhi's most polluted area Archived 19 January 2010 at the Wayback Machine, 25 December 2009, The Indian Express
- Najafgarh drain 11th among highly polluted industrial clusters Archived 1 July 2012 at archive.today, 25 December 2009, The Times of India
- drain causes less pollution in Yamuna now[permanent dead link], 4 July 2006, The Indian Express
- "Geography of Haryana - Map, Shivaliks, Ghaggar, Yamuna, Saraswati, Morni - India". haryana-online.com. Archived from the original on 1 February 2016.
- Siwach, Sukhbir (7 December 2014), "Haryana to meet Rajasthan over stopping of river waters", The Times of India, archived from the original on 5 February 2016, retrieved 12 November 2015
- Sudhir Bhargava,"Location of Brahmavarta and Drishadwati River is important to find earliest alignment of Saraswati River", International Conference, 20–22 Nov 2009, "Saraswati-a perspective" pages 114–117, Kurukshetra University, Kurukshetra, Organised by: Saraswati Nadi Shodh Sansthan, Haryana.
- "Western Yamuna Canal Major Irrigation Project JI01653 -". india-wris.nrsc.gov.in. Archived from the original on 13 November 2017. Retrieved 4 December 2017.
- "National Portal of India". india.gov.in. Archived from the original on 7 February 2009.
- "PIB Press Releases". pib.nic.in. Archived from the original on 1 March 2017. Retrieved 4 December 2017.
- Ramtanu Maitra: The Indira Gandhi Canal: greening the desert in India EIR Volume 14, Number 7, 13 February 1987
- "Kaushalya Dam". Hills of Morni. 13 December 2012. Archived from the original on 23 May 2014. Retrieved 14 June 2014.
- Tak, Prakash C.; Jagdish P. Sati; Anjum N. Rizvi (April 2010). "Status of waterbirds at Hathnikund Barrage wetland, Yamunanagar District, Haryana, India" (PDF). p. 841. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 March 2012. Retrieved 10 July 2011.
- Haberman, David L. (2006). River of love in an age of pollution: the Yamuna River of northern India. University of California Press. p. 78. ISBN 978-0-520-24789-5. Retrieved 2 June 2011.
- Peck, Lucy (2005). Delhi - A thousand years of Building. Suraj Kund dam and Surajkund tank. New Delhi: Roli Books Pvt Ltd. p. 29. ISBN 81-7436-354-8. Archived from the original on 12 March 2006. Retrieved 5 September 2009.
One of the two significant structures in the area, the dam lies about 1 km [0.62 mi] to the north of the Anangpur village. A path from the main village street will lead you in to flat pastureland. Head for the small rocky hill ahead of you and climb over it. On the other side is another flat area, rather thickly covered in thorn trees. It is worth finding a way through them to the dam that straddles the gap between the two nearby hills. The dam is an impressive edifice 50 m [160 ft] wide and 7 m [23 ft] high built from accurately hewn quartzite blocks.---There is a passage for the egress of water at the level of the ground on the dammed side. The flat land across which you have walked is clearly caused by centuries of silt deposits in the lake that once existed behind this dam. The land around has been vwey heavily quarried recently, so further archaeological finds are unlikely.
- Madan Mohan. "Spatial Data Modeling in GIS for Historical Restoration and Conservation of Cultural Heritage of Seven Cities of Delhi" (PDF). Department of Geography, Faculty of Natural Sciences, Jamia Millia Islamia (Central University) New Delhi, India. Retrieved 7 September 2009. [dead link]
- Sir William Wilson Hunter, India Office (1908), Imperial gazetteer of India, Clarendon Press, 1908, archived from the original on 29 September 2013, retrieved 13 November 2017,
... It was agreed between the British Government and the State of Bikaner that the Dhanur lake, about 8 miles from Sirsa, should be converted into a reservoir by the construction of a masonry weir at Otu ... two canals, the northern and southern ... constructed with famine labor in 1896-7 ... 6.3 lakhs, of which 2.8 lakhs was debited to Bikaner ...
- Mukesh Bhardwaj (7 April 2002), "Tau here, Tau there, Tau everywhere", The Indian Express, retrieved 28 November 2010,
... The prestigious Panipat Thermal Plant was named after Devi Lal, as was the new tourist complex at Ottu weir in Sirsa ...
- "बस साल भर बाद खेतों की प्यास बुझाएगी ओटू झील (Ottu reservoir will begin quenching the thirst of fields in only a year)", Dainik Jagran, 27 May 2010, archived from the original on 26 July 2011, retrieved 28 November 2010,
... किसानों की समस्या से निजात दिलाने में सहायक ओटू झील की याद बरबस किसानों व सिंचाई विभाग को आना लाज़िमी है। सिंचाई विभाग ने किसानों के हित को ध्यान में रखते हुए झील की खुदाई की गति तेज़ कर दी है (it is obvious that the suffering farmers and the irrigation department would look to the Ottu reservoir. Mindful of the farmers' interests, the irrigation department has accelerated the work to deepen Ottu reservoir) ...
- "Badkhal". Haryana Tourism, Government of Haryana. Archived from the original on 2 March 2014. Retrieved 18 March 2014.
- "Delhi's water bodies face threat of extinction". India Today. 1 March 2014. Archived from the original on 7 November 2017. Retrieved 18 March 2014.
- "Lakhs take dip in Brahma Sarovar on Occasion of Solar Eclipse". oneindia.in. United News of IndiaI. 29 March 2006. Archived from the original on 25 October 2014. Retrieved 25 October 2014.
- Dutt, K.G. (23 August 1998). "Three hundred thousand take holy dip". The Tribune India. Archived from the original on 25 October 2014. Retrieved 25 October 2014.
- "Religious Places in Kurukshetra - Brahma Sarovar". Kurukshetra district website. Archived from the original on 29 July 2014. Retrieved 8 August 2014.
- "Title: The Tribune - Hisar Bluebird lake, Published 23 December 2014. Retrieved 26 March 2016". Archived from the original on 21 August 2017. Retrieved 4 December 2017.
- "Blue Bird (Hisar)". 11 October 2011. Archived from the original on 11 October 2011. Retrieved 4 December 2017.
- Damdama lake Archived 27 November 2018 at the Wayback Machine, official website.
- Rajiv Tiwari, "Delhi A Travel Guide" Archived 27 November 2018 at the Wayback Machine, ISBN 9798128819703.
- Page 153, Tourism: Theory, Planning, and Practice, By K.K. Karma, Krishnan K. Kamra, Published 1997, Indus Publishing, ISBN 81-7387-073-X
- Sharma, Y.D (2001). Delhi and its Neighbourhood. Surjakund and Anagpur Dam. New Delhi: Archaeological Survey of India. p. 100 in 161. Archived from the original on 31 August 2005. Retrieved 5 September 2009.
Page 100: Suraj Kund lies about 3 km south-east of Tughlaqabad in district Gurgaon---The reservoir is believed to have been constructed in the tenth century by King Surjapal of Tomar dynasty, whose existence is based on Bardic tradition. Page 101: About 2 km south-west of Surajkund, close to the village of Anagpur (also called Arangpur is a dam ascribed to Anagpal of the Tomar Dynasty, who is also credited with building the Lal Kot
- "Ticketed Monuments – Haryana: Suraj Kund". National Informatics Centre, Government of India. Archived from the original on 11 October 2009. Retrieved 5 September 2009.
- Page 149, India: A Travel Guide, By B.R. Kishore, published 2001, Diamond Pocket Books (P) Limited, ISBN 81-284-0067-3
- "List of zoos who have submitted their master plan" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 4 December 2017.
- "Protected Area". haryanaforest.gov.in. Archived from the original on 12 May 2014. Retrieved 4 December 2017.
- "Haryana to develop 50-60 small lakes, water bodies in NCR: Manohar Lal Khattar" Archived 7 November 2017 at the Wayback Machine, Indian Express, 1 November 2017.
- "Haryana to constitute pond management authority " Archived 7 November 2017 at the Wayback Machine, Business Standard, 1 November 2017.
- "Sohna Hot Spring." Archived 4 November 2017 at the Wayback Machine, The Tribune.
- "Hotel Detail - Haryana Tourism Corporation Limited". haryanatourism.gov.in. Archived from the original on 13 February 2017. Retrieved 4 December 2017.
- 2004, "Records, Volume 135, Part 1." Archived 27 November 2018 at the Wayback Machine, Geological Survey of India, Page 144.
- "Station: Gurgaon Climatological Table 1981–2010" (PDF). Climatological Normals 1981–2010. India Meteorological Department. January 2015. pp. 305–306. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 February 2020. Retrieved 1 March 2020.
- "Extremes of Temperature & Rainfall for Indian Stations (Up to 2012)" (PDF). India Meteorological Department. December 2016. p. M64. Archived from the original (PDF) on 5 February 2020. Retrieved 1 March 2020.
- "State animals, birds, trees and flowers" (PDF). Wildlife Institute of India. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 June 2007. Retrieved 5 March 2012.
- Welcome To Our Website, Haryana Forest Department, archived from the original on 27 March 2018, retrieved 1 December 2018
- Flora and Fauna, archived from the original on 1 January 2016, retrieved 12 November 2015
- Conservation of Wildlife, archived from the original on 27 March 2018, retrieved 1 December 2018
- Fauna of Haryana, archived from the original on 2 December 2015
- Parks, Reserves and Other Protected Areas in Haryana, archived from the original on 12 May 2014, retrieved 11 May 2014
- "Protected Area". haryanaforest.gov.in. Archived from the original on 12 May 2014. Retrieved 4 August 2016.
- "From Punjab to Patna pollution spreads.", Dainik Jagran, 12 November 2017.
- Reorganisation of Haryana divisions Archived 29 December 2017 at the Wayback Machine, Daily Pioneer, 3 January 2017.
- Haryana approves to create two new revenue divisions Archived 29 December 2017 at the Wayback Machine, 2 February 2017.
- Authority set up to rejig administrative units across Haryana Archived 29 December 2017 at the Wayback Machine, Times of India, 3 January 2017.
- Haryana approves to create two new revenue divisions Archived 29 December 2017 at the Wayback Machine, Web India, 2 February 2017.
- "One year later, Municipal Corporation of Manesar battling transfer of amenities". Hindustan Times. 24 December 2021. Retrieved 24 February 2022.
- Municipal taxes will be sanctioned to the weak bodies of the state, Dainik Jagran news Archived 19 January 2018 at the Wayback Machine
- Haryana establishes five police ranges Archived 29 December 2017 at the Wayback Machine, business Standard, 16 January 2017.
- Haryana Police, archived from the original on 11 August 2018, retrieved 1 May 2019
- "HC starts e-filing, gets Wi-Fi complex", The Tribune, Chandigarh, Tribune News Service, 1 December 2014, archived from the original on 6 March 2016, retrieved 24 January 2016
- "Digital India campaign: Panchkula comes out on top among all districts of Haryana". The Indian Express. 26 December 2015. Archived from the original on 16 March 2016. Retrieved 10 March 2016.
- "Government unveils Umang app for citizen services." Archived 17 April 2018 at the Wayback Machine, Economic Times, 23 November 2017.
- "Govt's Umang app finally sees the light of the day: All you need to know." Archived 1 December 2017 at the Wayback Machine, Business Standard, 23 November 2017.
- India's Top 12 Tech Cities: Digital Indian Cities Survey, 2016 Archived 5 December 2017 at the Wayback Machine, CEOWORLD magazine, Nov 2016.
- Report on Haryana Agriculture and Farmers' Welfare (PDF) (Report). Indian Council of Food and Welfare. p. 2.
- "About IARI". IARI. Archived from the original on 16 March 2015. Retrieved 11 June 2015.
- "Bhakra Dam Will Be Engineering Marvel". The Indian Express. 4 September 1955. p. 13. Retrieved 11 April 2017.
- Report on Haryana Agriculture and Farmers' Welfare (PDF) (Report). Indian Council of Food and Welfare. p. 2.
- "Murrah Buffalo". Archived from the original on 7 February 2018. Retrieved 1 December 2018.
- "Murrah buffalo sets record with 26.33 kg milk". The Tribune. 16 January 2016. Archived from the original on 13 August 2017. Retrieved 24 April 2016.
- "Andhra Pradesh farmer buys Haryana murrah buffalo for Rs 25L". The Times of India. 11 August 2013. Archived from the original on 20 December 2016. Retrieved 30 June 2014.
- "Rs 40-lakh-a-year hurrah for owner of this Murrah!". Hindustan Times. 17 February 2014. Archived from the original on 19 August 2014. Retrieved 30 June 2014.
- "CIRB annual report 2015-16" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 July 2017. Retrieved 4 December 2017.
- M Gupta, 2011, Ranking of Indian institutions in agriculture & allied sciences Archived 27 January 2018 at the Wayback Machine.
- Jagvir Singh Yadav, 1992, Evaluation of Agricultural Extension: A Study of Haryana, Page 44.
- Salim Ahmed Lalli, 2007, Infrastructure and agricultural development in Haryana: policy implications.
- "The Tribune, Chandigarh, India - Delhi and neighbourhood". The Tribune. Archived from the original on 13 June 2007. Retrieved 7 February 2008.
- "File not found". Archived from the original on 22 December 2015. Retrieved 11 March 2018.
- Manohar, Asit (26 March 2012). "IOC Faridabad unit to pump in bio-fuel; R&D unit gearing to reduce pressure on conventional fuel". The Times of India. Archived from the original on 8 December 2015. Retrieved 11 March 2018.
- "金牛配资_炒股配资平台_ 免息配资公司". lntgulf.com. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016.
- Abhishek Law. "Eye-wear e-tailer Lenskart looks at 150% growth this fiscal". Business Line. Archived from the original on 11 February 2016. Retrieved 11 March 2018.
- "Faridabad: Rents climbing, sleepy town is hot property". The Times of India. Archived from the original on 22 June 2015. Retrieved 11 March 2018.
- Hisar aerodrome being considered for international airport, says MLA Archived 11 December 2014 at the Wayback Machine, HT Correspondent, Hindustan Times. Retrieved 2 December 2014.
- Haryana to develop international airport at Hisar Archived 19 October 2017 at the Wayback Machine, TravelBizMonitor Archived 29 November 2017 at the Wayback Machine, Retrieved in March 2016.
- State shelves Hisar airport cargo project Archived 19 October 2017 at the Wayback Machine, The Tribune, 29 May 2015.
- "Savitri Jindal and family". Forbes. Archived from the original on 4 July 2012. Retrieved 13 July 2012.
- "Haryana culture". Indian mirror. Archived from the original on 27 August 2015. Retrieved 31 July 2015.
- "OSRAM". Archived from the original on 13 May 2008. Retrieved 4 December 2017.
- "Atlas Cycles (Haryana) Ltd., Sonepat (India)". atlascyclesonepat.com. Archived from the original on 16 December 2017. Retrieved 4 December 2017.
- "ECE Industries Ltd". eceindustriesltd.com. Archived from the original on 29 November 2017. Retrieved 4 December 2017.
- "Article Window". 5 February 2011. Archived from the original on 27 November 2018. Retrieved 5 February 2011.
- "Haryana showpiece millennium city Gurgaon's 'powerless' original residents suffer". India.com. 1 September 2014. Archived from the original on 24 September 2015. Retrieved 25 February 2015.
- Tanushree Roy Chowdhury (22 December 2010). "Villagers fume after Haryana CM skips KMP meet". The Times of India. TNN. Archived from the original on 2 January 2017. Retrieved 7 February 2011.
- "Pin Code of Manesar Gurgaon". citypincode.in. Archived from the original on 9 March 2014. Retrieved 9 March 2014.
- General Information, archived from the original on 9 September 2012
- "HPGCL power plant capacity". Archived from the original on 6 December 2017. Retrieved 5 December 2017.
- "Haryana aims to install solar plants to replace old thermal plants", The Economic Times, 15 March 2016, archived from the original on 5 April 2016, retrieved 24 March 2016
- "Prime Minister Dr. Manmohan sigh Lays Foundation Stone of 2800 MW Gorakhpur Haryana Anu Vidyut Pariyojana (Nuclear Power Project)". Press Information Bureau, Government of India. 13 January 2014. Archived from the original on 22 February 2014. Retrieved 6 February 2014.
- Gorakhpur nuclear power plant makes headway Archived 21 September 2017 at the Wayback Machine. Down To Earth. 20 September 2012. Retrieved 2 April 2016.
- "List of State Highways in Haryana". Haryana Samanya Gyan. 2 September 2017. Archived from the original on 4 November 2018. Retrieved 4 November 2018.
- "Single agency to handle road repair work from January 1" Archived 29 December 2017 at the Wayback Machine, Tribune, 29 December 2017.
- "Why Haryana? - Economic Infrastructure". Archived from the original on 10 April 2009.
- "KMP Expressways to be completed by 2009". The Indian Express. Archived from the original on 15 March 2007.
- "NH-2 widening to claim 25,000 trees in Faridabad dist | india". Hindustan Times. 6 June 2012. Archived from the original on 17 November 2015. Retrieved 3 November 2015.
- Address by The President of India to the Joint sitting of Parliament 2014 (PDF), archived from the original (PDF) on 14 July 2014
- "Eastern DFC". Archived from the original on 26 November 2017. Retrieved 4 December 2017.
- "Western DFC". Archived from the original on 3 December 2017. Retrieved 4 December 2017.
- "Bikaner Division map and history" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 29 December 2017. Retrieved 29 December 2017.
- "Overview of Bikaner Division" (PDF). North Western Railway. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 May 2014. Retrieved 7 May 2014.
- "Jaipur division network map" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 29 December 2017. Retrieved 29 December 2017.
- "Delhi division map and history". Archived from the original on 7 May 2014. Retrieved 29 December 2017.
- "Zones and their Divisions in Indian Railways" (PDF). Indian Railways. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 March 2015. Retrieved 13 January 2016.
- "Ambala Railway Division". Northern Railway zone. Railway Board. Archived from the original on 18 April 2014. Retrieved 13 January 2016.
- "Statement showing Category-wise No.of stations in IR based on Pass. earning of 2011" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 January 2016. Retrieved 15 January 2016.
- "PASSENGER AMENITIES - CRITERIA= For Categorisation of Stations" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 15 January 2016.
- "NCR Zone map". Archived from the original on 30 December 2017. Retrieved 29 December 2017.
- "North Central Railways / Indian Railways Portal". ncr.indianrailways.gov.in. Archived from the original on 7 July 2012. Retrieved 4 December 2017.
- Ambala Division map and history Archived 18 April 2014 at the Wayback Machine.
- "NCR's longest Metro line in Faridabad | delhi". Hindustan Times. 23 January 2012. Retrieved 3 November 2015.[permanent dead link]
- "Projects - Delhi - Faridabad Elevated Expressway Project (dfskyway TM) (NH - 2)". HCC Infrastructure. 29 November 2010. Archived from the original on 1 January 2016. Retrieved 3 November 2015.
- "Egovonline.net". Archived from the original on 30 March 2012.
- "Punjabnewsline.com". Archived from the original on 1 January 2008.
- "The Tribune India". The Tribune. Archived from the original on 27 June 2009. Retrieved 6 February 2008.
- "Haryana News - Haryana News Live - Haryana Hindi News - Haryana Latest News | Hari Bhoomi". haribhoomi.com.
- State Wise Information, National Rural Health Mission, archived from the original on 15 May 2013
- Census 2011, Chapter 6 (State of Literacy) (PDF), pp. 114–117, archived (PDF) from the original on 6 July 2015, retrieved 17 November 2015
- "In Haryana, Gurgaon tops literacy rate but has worst sex ratio", The Indian Express, 23 May 2013, archived from the original on 7 June 2013, retrieved 3 November 2015
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 May 2014. Retrieved 15 May 2013.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - History, Haryana Board of School Education, archived from the original on 24 December 2015, retrieved 23 December 2015
- "Management Information System - Reports". hryedumis.gov.in. Archived from the original on 14 December 2017. Retrieved 4 December 2017.
- "Haryana Education stats: aided private schools, 2015-2016" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 October 2017. Retrieved 4 December 2017.
- "Haryana Education stats: Recognized unaided schools 2015-2016" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 31 October 2017. Retrieved 4 December 2017.
- "Haryana Education stats: list of unrecognized unaided schools, 2015-2016" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 October 2017. Retrieved 4 December 2017.
- Thakur, Bhartesh Singh (23 September 2019). "A first: Haryana has more women than men pursuing higher education". The Tribune.
- Haryana is growing rapidly in higher education, 299 colleges in small state, Jagram Archived 19 January 2018 at the Wayback Machine, 17 January 2018.
- "About HAU". Haryana Agricultural University. Archived from the original on 12 May 2012. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- "Vision 2030" (PDF). National Research Centre on Equines. Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 September 2012. Retrieved 7 June 2012.
- "Central sheep breeding farm". Department of Animal Husbandry, Dairying & Fisheries, GoI. Archived from the original on 22 November 2012. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- "Climate of Hisar". PPU. Archived from the original on 5 May 2012. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- "About us". Northern Region Farm Machinery Training and Testing Institute. Archived from the original on 16 September 2011. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- "About CIRB". Central Institute for Research on Buffaloes. Archived from the original on 13 September 2012. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- "Official website". Maharaja Agrasen Medical College. Archived from the original on 26 April 2012. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- "Under the Digital India initiative: Software Technology Park of India", The Indian Express, 28 February 2016, archived from the original on 10 March 2016, retrieved 10 March 2016
- "National Committee for Linguistic Minorities" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 18 October 2017. Retrieved 4 December 2017.
- "MizoramExpress.com is available at DomainMarket.com". MizoramExpress.com is available at DomainMarket.com. Archived from the original on 26 November 2010.
- Official site for the 33rd National Games 2007, Guwahati Archived 19 October 2009 at the Wayback Machine
- "Nahar Singh Stadium - India - Cricket Grounds - ESPN Cricinfo". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 4 January 2009. Retrieved 7 February 2008.
- "Tau Devi Lal Cricket Stadium - India - Cricket Grounds - ESPN Cricinfo". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 8 June 2008. Retrieved 7 February 2008.
- News Details, Office of Chief Minister of Haryana, archived from the original on 1 July 2017, retrieved 1 December 2018
- GoH 2015, p. 27.
- Yadav, Bhupendra (31 October 2010). "Why Haryana is India's mine for medals". The Times of India. Retrieved 26 July 2020.
Sources
- Haryana Sports and Physical Fitness Policy (PDF), Government of Haryana, 12 January 2015, archived from the original (PDF) on 17 November 2015, retrieved 13 November 2015
- Atul Kumar Sinha; Abhay Kumar Singh, eds. (2007), Udayana New Horizons in History, Classics and Inter-Cultural studies, Anamika Publishers, ISBN 978-81-7975-168-8
- National Disaster Risk Reduction Portal - Haryana (PDF), National Institute of Disaster Management, archived from the original (PDF) on 9 September 2016, retrieved 12 November 2015
- Sharma, Suresh K (2006). Haryana: Past and Present. New Delhi: Mittal Publications. p. 763. ISBN 81-8324-046-1. Retrieved 11 July 2012.
- Khanna, C. L. (2008). Haryana General Knowledge. Agra: Upkar Prakashan. p. 75. ISBN 978-81-7482-383-0. Retrieved 11 July 2012.
- Yadav, Ram B. (2008). Folk Tales & Legends of Haryana. Gurgaon: Pinnacle Technology. p. 305. ISBN 978-81-7871-162-1. Retrieved 11 July 2012.
- Mittal, Satish Chandra (1986). Haryana, a Historical Perspective. New Delhi: Atlantic Publishers & Distributors. p. 183. Retrieved 11 July 2012.
- Singh, Mandeep; Kaur, Harvinder (2004). Economic Development of Haryana. New Delhi: Deep and Deep Publications. p. 234. ISBN 81-7629-558-2. Retrieved 11 July 2012.
- Gandhi, Mahatma (1977). Gandhiji and Haryana: A collection of his speeches and writings pertaining to Haryana. Usha Publications. p. 158. Retrieved 11 July 2012.
- Phadke, H. A. (1990). Haryana, ancient and medieval. Harman Publishing House. p. 256. ISBN 81-85151-34-2. Retrieved 11 July 2012.
- Singh, Chattar (2004). Social and economic change in Haryana. National Book Organisation. p. 252. ISBN 81-87521-10-4. Retrieved 11 July 2012.
- Yadav, Kripal Chandra (2002). Modern Haryana: History and culture, 1803–1966. Manohar Publishers & Distributors. p. 320. ISBN 81-7304-371-X. Retrieved 11 July 2012.
- Rai, Gulshan (1987). Formation of Haryana. B.R. Publishing Corporation. p. 223. ISBN 81-7018-412-6. Retrieved 11 July 2012.
- Handa, Devendra (2004). Buddhist remains from Haryana. Sundeep Prakashan. p. 97. ISBN 81-7574-153-8. Retrieved 11 July 2012.
- Haryana at a glance: Statistical overview & development indicators. Jagran Research Centre. 2007. p. 157. ISBN 9788186821428. Retrieved 11 July 2012.
- Singh, Chander Pal (2003). Early medieval art of Haryana. Koshal Book Depot. p. 168. ISBN 81-86049-07-X. Retrieved 11 July 2012.
- Handa, Devendra (2006). Sculptures from Haryana: Iconography and style. Indian Institute of Advanced Study. p. 286. ISBN 81-7305-307-3. Retrieved 11 July 2012.
- Journal of Haryana Studies. Kurukshetra: Kurukshetra University. 2008. Retrieved 11 July 2012.
- Harvey, Bill; Harvey, William; Devasar, Nikhil; Grewal, Bikram; Oriental Bird Club (2006). Atlas of the birds of Delhi and Haryana. Rupa & Co. p. 352. ISBN 81-291-0954-9. Retrieved 11 July 2012.
External links
- Government
- The Official Site of the Government of Haryana
- Official Tourism Site of Haryana, India
- Haryana Community website
- General information
 Geographic data related to Haryana at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to Haryana at OpenStreetMap
Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии










