world.wikisort.org - Philippines
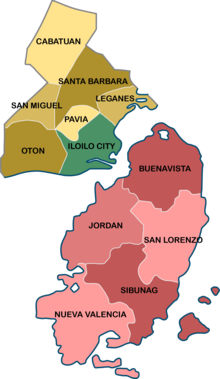
Metropolitan Iloilo–Guimaras (Hiligaynon: Kaulohan nga Iloílo–Guimarás; Filipino: Kalakhang Iloílo–Guimarás), also shortened as Metro Iloilo–Guimaras or simply MIG, is a metropolitan area in the Visayas in the Philippines. It consists of the highly urbanized city of Iloilo City; the regional agro-industrial center of Pavia; the municipalities of Cabatuan, Leganes, Oton, San Miguel, and Santa Barbara; and the neighboring island province of Guimaras, with its five municipalities of Jordan, Buenavista, Nueva Valencia, San Lorenzo, and Sibunag.
Metro Iloilo–Guimaras
Kaulohan nga Iloilo–Guimaras Kalakhang Iloilo–Guimaras | |
|---|---|
Metropolitan area | |
| Metropolitan Iloilo–Guimaras | |
 Skyline of Mandurriao district, Iloilo City | |
 Seal | |
| Nickname: MIG | |
 Map of Metro Iloilo–Guimaras (in red) including the province of Iloilo highlighted in light orange. | |
 | |
| Coordinates: 10°43′N 122°34′E | |
| Country | Philippines |
| Region | Western Visayas (Region VI) |
| Province |
|
| Managing entity | Metro Iloilo–Guimaras Economic Development Council |
| Established |
|
| Cities and Municipalities | 12
|
| Government | |
| • Type | Metropolitan government |
| • Body | Metro Iloilo–Guimaras Economic Development Council |
| • MIGEDC Chairman | Jerry Treñas (Mayor of Iloilo City) |
| • Executive Director | Velma Jane Lao |
| Area | |
| • Total | 1,105.53 km2 (426.85 sq mi) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 1,007,945 |
| • Density | 910/km2 (2,400/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (PST) |
| Languages | Hiligaynon, Kinaray-a, English |
| Website | www |
Metro Iloilo–Guimaras is the only officially recognized metropolitan area in the Western Visayas region. It is the second largest metropolitan area in the Visayas after Metro Cebu, being the center of trade and commerce in the region. In the 2020 census, it has a total population of 1,007,945 people and a total land area of 1,105.53 square kilometres (426.85 sq mi).
The Metro Iloilo–Guimaras Economic Development Council (MIGEDC) is the agency responsible for the economic growth and development plans for Metro Iloilo and province of Guimaras. It was created by virtue of Executive Order 559, signed by President Gloria Macapagal-Arroyo on August 28, 2006.
Cities and municipalities
Metro Iloilo–Guimaras consists of one highly urbanized city of Iloilo City, which serves as the central core of the metropolitan, and six municipalities in Iloilo Province (Cabatuan, Leganes, Pavia, Oton, San Miguel, Santa Barbara) and five municipalities in Guimaras Province (Buenavista, Jordan, Nueva Valencia, San Lorenzo, Sibunag).[2]
 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Economy
The economy of Metro Iloilo alone is one of the largest in the Visayas and the country. It serves as a center for trade, commerce, finance, technology, medical tourism, hospitality, real estate, tourism, education, and industry in the Western Visayas region. Major industries in the metropolis include the management of port facilities, telecommunications infrastructure and utilities, agriculture, banking and finance, retail trading, real estate, tourism, and business process outsourcing (BPO).[3]
Aside from Iloilo City, the municipalities of Pavia, Oton, and Santa Barbara also serve as the three major commercial and business centers in the metropolitan area, where the large mixed-use development townships are mostly located outside Iloilo City.
Pavia, also being the agro-industrial center of the region, has 39 manufacturing establishments producing various products intended for the domestic and export markets. Among the important products are farm implements, milled rice, poultry and livestock feeds, noodles, soft drinks, dressed chicken, cooking oil, furniture, concrete products, polyurethane foam, and industrial and medical gases. Pavia is home to a number of prestigious manufacturing establishments. Among the biggest investors locators are; Coca-Cola Bottlers, Phils., Vitarich Corporation, Pryce Gases, Inc. Mandaue Foam Industries, Panay Tropical Grains Milling Corp., Jaspe Light Steel Indus.[4]
The province of Guimaras is mainly agricultural, with mangoes, palay, coconuts, livestock, poultry, and fishing as major products. Its industries include tourism, fruit processing, coconut processing, fish farming, handicrafts, mining, quarrying, and lime production.
As the major economic hub and financial center of Western Visayas, an adequate and growing number of banks are establishing branches, leading to the metropolitan area having the third-most bank savings deposits and accounts in the Philippines.[5]
Infrastructure developments
Roads

The Sen. Benigno S. Aquino Jr. Avenue (Diversion Road), Mc Arthur Drive, Cong. Narciso Monfort Boulevard, Gen. Luna Street, CJ Ramon Avancena Street, E. Lopez Street, Pres. Corazon C. Aquino Avenue (Circumferencial Road 1 or C1), Iznart Street, and Mulle Loney Drive are Metro Iloilo's major roads. Sen. Benigno S. Aquino Jr. Avenue was renovated and widened into an 8-lane main road with a protected bike lane and a 2-lane service road. It connects Iloilo City, Pavia, Santa Barbara, and the Iloilo International Airport.
There are currently two operating vehicular overpasses or flyovers in Metro Iloilo; the Infante flyover and the Jalandoni flyover, both along General Luna Street in Iloilo City Proper. There are also a total of four new flyovers currently under construction. The two four-lane Ungka and Aganan flyovers, both located in Pavia; and the two two-lane Hibao-an and Buhang flyovers, crossing Mandurriao-San Miguel Road in Mandurriao district and Iloilo-Capiz Road in Jaro district, respectively, both along the Iloilo Circumferential Road.[6]
The existing President Corazon C. Aquino Avenue, also known as Circumferencial Road 1 or C1, covers roads from Balabago, Jaro to San Jose, Arevalo, Iloilo City. There are also three new circumferential roads that are under construction within Metro Iloilo. Circumferential Road 2 (C2), from coastal Leganes to Cabugao, Pavia, and all the way to the Oton-San Jose San Miguel Road; Circumferential Road 3 (C3), from the coastal road Zarraga-Dumangas boundary to Zarraga town proper and all the way to Sta. Barbara; and Circumferential Road 4 (C4), from Barotac Nuevo to Southern Iloilo.[7]
The construction of the Iloilo–Guimaras Bridge, a component of the Panay-Guimaras-Negros Bridge that will connect the entire metropolitan area as well as the whole Western Visayas region, is well underway.[8]
Airport
Iloilo International Airport (Iloilo Airport) is the airport serving the general area of Iloilo City, the capital city of the province of Iloilo and the regional center of the Western Visayas region in the Philippines. It opened its doors to commercial traffic on June 14, 2007 after a decade of planning and construction, replacing Mandurriao Airport in Iloilo City proper which had been in service for over seventy years. As a result, the new airport inherited its IATA and ICAO airport codes, as well as its position as the fourth-busiest airport in the Philippines, from its predecessor. In addition to being the first airport in both Western Visayas and the island of Panay to be built to international standards, it is considered one of four international airports in the Visayas with international flights to Hong Kong and Singapore.
The new Iloilo International Airport is located in Cabatuan;[9] specifically in Barangay Tabucan, Barangay Gaub, Barangay Duyan-Duyan and Barangay Manguna, all in Cabatuan. The airport can be reached either from the Cabatuan access roads (Barangay Tabucan and Barangay Tiring, Cabatuan) or from the Pavia-Santa Barbara-Cabatuan (Barangay Duyan-Duyan, Cabatuan) access road.[9] The airport complex consists of a single runway, various administrative and maintenance buildings, waste sorting and water treatment facilities, a power generating station, a cargo terminal and a main passenger terminal. Its location on the Tomas Confesor Highway, a major highway transversing the island, makes the airport accessible from all parts of Iloilo and Panay by road, while its proximity to the currently defunct Panay Railways network could potentially link the airport to the rest of Panay by rail.
Seaport

The Port of Iloilo is the port serving the general area of Iloilo and the rest of Panay Island and Guimaras Island. There are 5 seaports in Metro Iloilo, these are the Iloilo Ferry Port and Terminal Complex, Iloilo River Port and Terminal Complex, Iloilo Domestic Port and Terminal Complex, Dumangas Ro - Ro Port and Terminal Complex and The Iloilo Commercial Port Complex which is located on 20.8 hectares of reclaimed land. It has facilities that include 11,400 sq. meters of open space for operations, supplemented by a backup area of 97,000 sq. meters, a crane, rails of 348 lineal meters, roll-on/roll-off support, a freight station, and a 720 sq. meter passenger shed. The port complex is ideal for ships plying international routes having a berth length of 400 meters, a width of 26.26 meters and a berthing depth of 10.50 meters.
There are a number of shipping companies that use the Port of Iloilo, among them, the Aboitiz Shipping Company, Amigo Shipping Company, New Panay Shipping Company, Negros Navigation Company, Sulpicio Lines, William Lines, and Trans-Asia Shipping Lines. Fast ferries serve Iloilo-Bacolod routes eight times daily. Negros Navigation and Superferry dock to the city where it serves routes going to Manila, Bacolod, Cebu, Zamboanga and Cagayan de Oro City.
Fishing Port
The only fishing port complex in the Visayas, the Iloilo Fish Port Complex is located at the mouth of the Batiano River on a reclaimed 20.5 hectare land.[10]
Public-transport terminals
Iloilo City boast of 5 integrated transport terminals, these are the Northern Iloilo Integrated Jeepney and Bus Terminal in Tagbac, Jaro. The Central Line Jeepney and Bus Terminal in Ungka, Jaro. The Upland Jeepney and Bus Terminal in Mandurriao. The Souther Coast Jeepney and Bus Terminal in Mohon, Arévalo and the North Coastal Jeepney and Bus Terminal in Ingore, La Paz.
Railway
Proposed revival of the currently defunct Panay Railways, re-connect Iloilo City to Santa Barbara, which has a railway station and is home to the entrance of Iloilo International Airport in Cabatuan.[11]
Education
Metro Iloilo–Guimaras serves as one of the centers of education in the Philippines. There are a large number of educational institutions in the area serving the region of Western Visayas and other neighboring provinces. It has one of the highest numbers of universities in the country, with a total of nine universities. The following list represents some of the notable institutions in the metro:
- ACSI College Iloilo
- Cabalum Western College
- Central Philippine University
- Colegio de San Jose
- Colegio del Sagrado Corazon de Jesus
- Guimaras State University
- Hua Siong College of Iloilo
- Iloilo Doctors' College
- Iloilo Science and Technology University
- John B. Lacson Foundation Maritime University
- St. Paul University Iloilo
- St. Therese – MTC colleges
- University of Iloilo
- University of San Agustin
- University of the Philippines Visayas
- West Visayas State University
- Western Institute of Technology
Metro Iloilo–Guimaras Economic Development Council

The Metro Iloilo–Guimaras Economic Development Council, or MIGEDC, was formally established by President Gloria Macapagal-Arroyo through Executive Order No. 559, signed on August 28, 2006. It evolved from the Metro Iloilo Development Council (MIDC) that was earlier established by the City of Iloilo and four neighboring municipalities of Leganes, Oton, Pavia, and San Miguel on February 9, 2001, and the Guimaras–Iloilo City Alliance (GICA) that was similarly established on May 22, 2005. Through Executive Order No. 559, the municipality of Santa Barbara became an addition together with the province of Guimaras. After the opening of the new Iloilo International Airport in the municipality of Cabatuan in 2007, the town was also added to the metropolitan.
During the MIGEDC press conference in March 2022, Iloilo City Mayor and MIGEDC Chairman Jerry P. Treñas revealed that the municipalities of Dumangas and Zarraga had expressed their intention to join the MIGEDC in the near future. Velma Jane Lao, MIGEDC Executive Director, is also on the work on the expansion of the council and will be confirming if the other municipalities that have long signified to join are still interested.[12]
As a strengthened task group, the MIGEDC formulates, implements, coordinates, and monitors programs, projects, and activities that support the Mega-Region Economic Development Strategic Framework of the National Government. It was designed to help address the area’s emerging problems brought about by rapid urbanization and the spatial development challenges of tourism and economic development. The MIGEDC is gearing up to become a Smart Metropolitan.
The MIGEDC is composed of the following:
- Mayor, Iloilo City as Chairperson
- Provincial Governor, Province of Guimaras as Co-Chairperson
- Mayor, Municipality of Pavia, Iloilo
- Mayor, Municipality of San Miguel, Iloilo
- Mayor, Municipality of Oton, Iloilo
- Mayor, Municipality of Leganes, Iloilo
- Mayor, Municipality of Sta. Barbara, Iloilo
- Mayor, Municipality of Cabatuan, Iloilo
- President, League of Municipalities, Province of Guimaras
See also
- Metro Manila
- Metro Cebu
References
- Census of Population (2020). Table B - Population and Annual Growth Rates by Province, City, and Municipality - By Region. PSA. Retrieved 8 July 2021.
- "Member Municipalities of Metro Iloilo–Guimaras". MIGEDC: Metro-Iloilo–Guimaras Economic Development Council. Retrieved 2009-09-07.
- "Iloilo City well poised for investment influx | National Competitiveness Council". www.competitive.org.ph. Retrieved 2022-08-31.
- "Pavia's Pride". ARANGKA PA, PAVIA!. 2008-12-12. Retrieved 2022-08-31.
- "Iloilo City draws more regional bank offices". SUNSTAR. 2022-06-30. Retrieved 2022-08-31.
- "You are being redirected..." www.panaynews.net. Retrieved 2022-08-31.
- Today, Iloilo (2020-01-17). "DPWH builds 'big-ticket road projects' in preparation for Iloilo-Guimaras bridge". Iloilo Today. Retrieved 2022-08-31.
- Marzan @inquirervisayas, Joey (2022-07-15). "Panay-Guimaras-Negros bridge may start soon, says Iloilo mayor". INQUIRER.net. Retrieved 2022-08-31.
- "Iloilo International Airport". IloiloAirport.com.
- "Iloilo Fish Port Complex". pfda.gov.ph. Retrieved 2022-08-31.
- Cervantes, Filane Mikee (2022-04-26). "Railways in Panay Island soon 'to be a reality': solon". www.pna.gov.ph. Retrieved 2022-08-31.
- Lena, Perla (March 24, 2022). "Iloilo City revitalizes Metro Iloilo, Guimaras dev't council". Philippine News Agency.
External links
- Metro Iloilo–Guimaras Economic Development Council – Official website
- Metro Iloilo–Guimaras Economic Development Council on Facebook
Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии