world.wikisort.org - Russia
Pechengsky District (Russian: Пе́ченгский райо́н; Finnish: Petsamo; Norwegian: Peisen; Northern Sami: Beahcán; Skolt Sami: Peäccam) is an administrative district (raion), one of the six in Murmansk Oblast, Russia.[1] As a municipal division, it is incorporated as Pechengsky Municipal District.[7] It is located in the northwest of the oblast, on the coast of the Barents Sea (by the Rybachy Peninsula, which is a part of the district) and borders Finland in the south and southwest and Norway in the west, northwest, and north. The area of the district is 8,662.22 square kilometers (3,344.50 sq mi).[3] Its administrative center is the urban locality (an urban-type settlement) of Nikel.[1] Its population was 38,920 (2010 Census);[4] 46,404 (2002 Census);[9] 59,495 (1989 Census).[10] The population of Nikel accounts for 32.8% of the district's total population.[4]
Pechengsky District
Печенгский район | |
|---|---|
District | |
 Landscape in Pechengsky District, August 2013 | |
 Location of Pechengsky District in Murmansk Oblast | |
| Coordinates: 69°32′N 31°12′E | |
| Country | Russia |
| Federal subject | Murmansk Oblast[1] |
| Established | July 21, 1945[2] |
| Administrative center | Nikel[1] |
| Government | |
| • Type | Local government |
| • Body | Council of Deputies[3] |
| Area | |
| • Total | 8,662.22 km2 (3,344.50 sq mi) |
| Population (2010 Census)[4] | |
| • Total | 38,920 |
| • Estimate (2018)[5] | 37,146 (−4.6%) |
| • Density | 4.5/km2 (12/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 81.6% |
| • Rural | 18.4% |
| Administrative structure | |
| • Administrative divisions | 1 Towns, 2 Urban-type settlements, 1 Territorial okrugs |
| • Inhabited localities | 1 Cities/towns, 2 Urban-type settlements[6], 14 Rural localities |
| Municipal structure | |
| • Municipally incorporated as | Pechengsky Municipal District[7] |
| • Municipal divisions[7] | 3 Urban settlements, 1 Rural settlements |
| Time zone | UTC+3 (MSK |
| OKTMO ID | 47615000 |
| Website | http://pechengamr.ru/ |
History
Russian settlement
The area was long inhabited by the indigenous Sami people. The border between Norway and Russia was not defined in terms of land, instead the Treaty of Novgorod (1326) specified which indigenous, nomadic families had to pay their taxes to which government. In 1533, the settlement of the Pechenga Monastery was defined as part of Russia.
The settlement of Pechenga was founded as the Pechenga Monastery in 1533 at the influx of the Pechenga River into the Barents Sea, 135 kilometers (84 mi) west of modern Murmansk, by St. Tryphon, a monk from Novgorod. Inspired by the model of the Solovetsky Monastery, Tryphon wished to convert the local Skolt Sami population to Christianity and to demonstrate how faith could flourish in the most inhospitable lands.
The area was resettled by the Pomors and other Russians. The present border between Norway and Russia was settled in 1826, and the development of the area considerably accelerated in the late 19th century, when the monastery was re-established there. The harbor of Liinakhamari in Petsamo was important for the Russian economy during World War I as the Baltic Sea was blocked by the Germans.
Finnish control
According to the 1920 Treaty of Tartu that followed Finnish occuрation of the region, Soviet Russia ceded the area of Pechenga (Petsamo Province) to Finland.[2]
Deposits of nickel were found in 1921, after Petsamo became a part of Finland. In 1934, the deposits were estimated at over five million tonnes. Mining operations were started in 1935 by Canadian and French corporations.
Construction of a road from Sodankylä through Ivalo to Liinakhamari started in 1916 and was completed in 1931. This made Petsamo a popular tourist attraction, as it was the only port by the Barents Sea reachable by automobile.
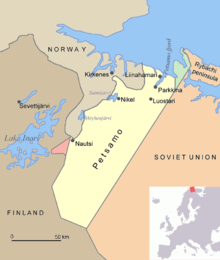
In the Winter War of 1939–1940, the Soviet Union briefly occupied Petsamo. In the following peace agreement, the Rybachy Peninsula, with the area of 321 square kilometers (124 sq mi), was the only part of Petsamo ceded to the Soviet Union, although the Soviets had occupied all of Petsamo during the Winter War.
In 1941, during World War II, Petsamo was used by Nazi Germany as a staging area for the offensive towards Murmansk. In 1944, the Red Army occupied Petsamo again, and this time Finland had to cede it to the Soviet Union as part of the Moscow Armistice signed on September 19, 1944 that halted fighting in the Continuation War.[2] The total ceded area was 8,965 square kilometers (3,461 sq mi). On July 21, 1945, the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union decreed the establishment of Pechengsky District with the administrative center in Nikel on the ceded territory and to include this district as a part of Murmansk Oblast.[2]
In 1947, Finland exchanged the remaining 169 square kilometers (65 sq mi) Rayakoski area, together with the Jäniskoski hydroelectric plant, for Soviet-confiscated German investments in Finland.
Retrocession to Russia
Following the Paris Peace Treaty, the local Skolt Sami were given the choice of staying in Soviet Russia or moving to Finland.[citation needed] Most opted to re-settle in Finland, but some chose to stay in Russia.[citation needed]
When Polyarny District was abolished on July 9, 1960, a part of its territory was transferred to Pechengsky District.[11]
On December 26, 1962, when the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the RSFSR decreed the reorganisation of the Soviets of People's Deputies and the executive committees of the krais, oblasts, and districts into the industrial and agricultural soviets, Murmansk Oblast was not affected and kept one unified Oblast Soviet and the executive committee.[2] Nevertheless, on February 1, 1963, the Decree by the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the RSFSR established the new structure of the districts of Murmansk Oblast, which classified Pechengsky District as rural.[2] However, this classification only lasted for less than two years.[2] The November 21, 1964 Decree by the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the RSFSR restored the unified Soviets of People's Deputies and the executive committees of the krais and oblasts where the division into the urban and rural districts was introduced in 1962, and the districts of Murmansk Oblast were re-categorized as regular districts again by the January 12, 1965 Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the RSFSR Decree.[2]
Economy
The district is important for its ice-free harbor, Liinakhamari, and the deposits of nickel.
See also
References
Notes
- Law #96-01-ZMO
- Administrative-Territorial Division of Murmansk Oblast, pp. 54–56
- Charter of Pechengsky District
- Russian Federal State Statistics Service (2011). Всероссийская перепись населения 2010 года. Том 1 [2010 All-Russian Population Census, vol. 1]. Всероссийская перепись населения 2010 года [2010 All-Russia Population Census] (in Russian). Federal State Statistics Service.
- "26. Численность постоянного населения Российской Федерации по муниципальным образованиям на 1 января 2018 года". Federal State Statistics Service. Retrieved January 23, 2019.
- The count of urban-type settlements may include the work settlements, the resort settlements, the suburban (dacha) settlements, as well as urban-type settlements proper.
- Law #539-01-ZMO
- "Об исчислении времени". Официальный интернет-портал правовой информации (in Russian). June 3, 2011. Retrieved January 19, 2019.
- Russian Federal State Statistics Service (May 21, 2004). Численность населения России, субъектов Российской Федерации в составе федеральных округов, районов, городских поселений, сельских населённых пунктов – районных центров и сельских населённых пунктов с населением 3 тысячи и более человек [Population of Russia, Its Federal Districts, Federal Subjects, Districts, Urban Localities, Rural Localities—Administrative Centers, and Rural Localities with Population of Over 3,000] (XLS). Всероссийская перепись населения 2002 года [All-Russia Population Census of 2002] (in Russian).
- Всесоюзная перепись населения 1989 г. Численность наличного населения союзных и автономных республик, автономных областей и округов, краёв, областей, районов, городских поселений и сёл-райцентров [All Union Population Census of 1989: Present Population of Union and Autonomous Republics, Autonomous Oblasts and Okrugs, Krais, Oblasts, Districts, Urban Settlements, and Villages Serving as District Administrative Centers]. Всесоюзная перепись населения 1989 года [All-Union Population Census of 1989] (in Russian). Институт демографии Национального исследовательского университета: Высшая школа экономики [Institute of Demography at the National Research University: Higher School of Economics]. 1989 – via Demoscope Weekly.
- Decree #741/18
Sources
- Мурманская областная Дума. Закон №96-01-ЗМО от 6 января 1998 г. «Об административно-территориальном устройстве Мурманской области», в ред. Закона №1953-01-ЗМО от 24 декабря 2015 г. «О внесении изменений в Закон Мурманской области "Об административно-территориальном устройстве Мурманской области"». Опубликован: "Мурманский Вестник", №10, стр. 3, 16 января 1998 г. (Murmansk Oblast Duma. Law #96-01-ZMO of January 6, 1998 On the Administrative-Territorial Structure of Murmansk Oblast, as amended by the Law #1953-01-ZMO of December 24, 2015 On Amending the Law of Murmansk Oblast "On the Administrative-Territorial Structure of Murmansk Oblast". ).
- Мурманская областная Дума. Закон №539-01-ЗМО от 2 декабря 2004 г. «О статусе, наименованиях и составе территорий муниципального образования Печенгский район и муниципальных образований, входящих в его состав», в ред. Закона №1156-01-ЗМО от 23 ноября 2009 г «Об упраздении некоторых населённых пунктов Мурманской области и внесении изменений в отдельные законодательные акты Мурманской области». Вступил в силу 1 января 2005 г. Опубликован: "Мурманский Вестник", №234, стр. 3, 7 декабря 2004 г. (Murmansk Oblast Duma. Law #539-01-ZMO of December 2, 2004 On the Status, Names, and Composition of the Territories of the Municipal Formation of Pechengsky District and of the Municipal Formations It Comprises, as amended by the Law #1156-01-ZMO of November 23, 2009 On the Abolition of Several Inhabited Localities of Murmansk Oblast and on Amending Several Legislative Acts of Murmansk Oblast. Effective as of January 1, 2005.).
- Совет депутатов муниципального образования Печенгский район. Решение №234 от 26 января 2006 г. «Устав муниципального образования Печенгский муниципальный район Мурманской области», в ред. Решения №165 от 10 декабря 2010 г «О внесении изменений в Устав муниципального образования Печенгский район Мурманской области, принятый Решением Совета депутатов муниципального образования Печенгский муниципальный район от 26.01.2006 №234, с изменениями от 10.03.2006 №246, от 05.05.2006 №40, от 14.11.2008 №396, от 30.10.2009 №542, от 18.06.2010 №67, от 17.09.2010 №94». Вступил в силу в соответствии с пунктами 1 и&nbps;2 статьи 69. Опубликован: "Печенга", №57, стр. 1–6, 27 мая 2006 г. (Council of Deputies of the Municipal Formation of Pechengsky District. Decision #234 of January 26, 2006 Charter of the Municipal Formation of Pechengsky Municipal District of Murmansk Oblast, as amended by the Resolution #165 of December 10, 2010 On Amending the Charter of the Municipal Formation of Pechengsky District of Murmansk Oblast, Adopted by the Decision of the Council of Deputies of the Municipal Formation of Pechengsky District No. 234 of January 26, 2006, revised by No. 246 of March 10, 2006, by No. 40 of May 5, 2006, by No. 396 of November 14, 2008, by No. 542 of October 30, 2009, by No. 67 June 18, 2010, by No. 94 of September 17, 2010. Effective as of the date set forth by the provisions of items 1 and 2 of Article 69.).
- Архивный отдел Администрации Мурманской области. Государственный Архив Мурманской области. (1995). Административно-территориальное деление Мурманской области (1920-1993 гг.). Справочник. Мурманск: Мурманское издательско-полиграфическое предприятие "Север".
- Президиум Верховного Совета РСФСР. Указ №741/18 от 9 июля 1960 г. «Об упразднении Полярного района, объединении Североморского городского и Териберского районного советов и переименовании Териберского района Мурманской области». Опубликован: "Ведомости ВС РСФСР", №25, ст. 371, 1960. (Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the Russian SFSR. Decree #741/18 of July 9, 1960 On the Abolition of Polyarny District, the Merger of Severomorsk Town and Teribersky District Soviets, and the Renaming of Teribersky District of Murmansk Oblast. ).
External links
 Media related to Pechengsky District at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Pechengsky District at Wikimedia Commons- Official website of Pechengsky District (in Russian)
- Unofficial website of Pechengsky District (in Russian)
- News of Pechengsky District (in Russian)
- SIIDA. From Petsamo to Inari (Skolt Sámi history)
На других языках
- [en] Pechengsky District
[ru] Печенгский район
Пе́ченгский райо́н — административно-территориальная единица в Мурманской области РФ. В границах района образован одноимённый муниципальный округ.Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии

